7-Dehydrocholesterol Encapsulated Polymeric Nanoparticles As a Radiation-Responsive Sensitizer for Enhancing Radiation Therapy
- PMID: 35304816
- PMCID: PMC9068268
- DOI: 10.1002/smll.202200710
7-Dehydrocholesterol Encapsulated Polymeric Nanoparticles As a Radiation-Responsive Sensitizer for Enhancing Radiation Therapy
Abstract
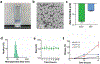
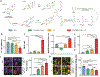
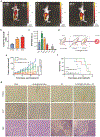
Therapeutics that can be activated by radiation in situ to enhance the efficacy of radiotherapy are highly desirable. Herein, 7-Dehydrocholesterol (7-DHC), a biosynthetic precursor of cholesterol, as a radiosensitizer, exploiting its ability to propagate the free radical chain reaction is explored. The studies show that 7-DHC can react with radiation-induced reactive oxygen species and in turn promote lipid peroxidation, double-strand breaks, and mitochondrial damage in cancer cells. For efficient delivery, 7-DHC is encapsulated into poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles, forming 7-DHC@PLGA NPs. When tested in CT26 tumor bearing mice, 7-DHC@PLGA NPs significantly enhanced the efficacy of radiotherapy, causing complete tumor eradication in 30% of the treated animals. After treatment, 7-DHC is converted to cholesterol, causing no detectable side effects or hypercalcemia. 7-DHC@PLGA NPs represent a radiation-responsive sensitizer with great potential in clinical translation.
Keywords: 7-dehydrocholesterol; colon carcinoma; nanoparticles; radiation therapy; radiosensitizers.
© 2022 Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
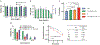
Similar articles
-
Polymeric nanoparticles for targeted radiosensitization of prostate cancer cells.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015 May;103(5):1632-9. doi: 10.1002/jbm.a.35300. Epub 2014 Aug 14. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2015. PMID: 25088162 Free PMC article.
-
Radiosensitization of TPGS-emulsified docetaxel-loaded poly(lactic-co-glycolic acid) nanoparticles in CNE-1 and A549 cells.J Biomater Appl. 2016 Mar;30(8):1127-41. doi: 10.1177/0885328215604081. Epub 2015 Nov 24. J Biomater Appl. 2016. PMID: 26608458
-
Hyaluronic acid-grafted PLGA nanoparticles for the sustained delivery of berberine chloride for an efficient suppression of Ehrlich ascites tumors.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2018 Jun;8(3):565-579. doi: 10.1007/s13346-018-0485-9. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2018. PMID: 29441466
-
PLGA-based nanoparticles as cancer drug delivery systems.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(2):517-35. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.2.517. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014. PMID: 24568455 Review.
-
Application of High-Z Nanoparticles to Enhance Current Radiotherapy Treatment.Molecules. 2024 May 22;29(11):2438. doi: 10.3390/molecules29112438. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38893315 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nanoparticle-based radiosensitization strategies for improving radiation therapy.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Feb 16;14:1145551. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1145551. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36873996 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanomedicine-based multimodal therapies: Recent progress and perspectives in colon cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2023 Jan 28;29(4):670-681. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v29.i4.670. World J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 36742173 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biodegradable copper-iodide clusters modulate mitochondrial function and suppress tumor growth under ultralow-dose X-ray irradiation.Nat Commun. 2024 Sep 16;15(1):8092. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-52278-6. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39285181 Free PMC article.
-
Advances in nanoparticle-based radiotherapy for cancer treatment.iScience. 2024 Dec 14;28(1):111602. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.111602. eCollection 2025 Jan 17. iScience. 2024. PMID: 39834854 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Abnormal changes in metabolites caused by m6A methylation modification: The leading factors that induce the formation of immunosuppressive tumor microenvironment and their promising potential for clinical application.J Adv Res. 2025 Apr;70:159-186. doi: 10.1016/j.jare.2024.04.016. Epub 2024 Apr 25. J Adv Res. 2025. PMID: 38677545 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Burbach JP, den Harder AM, Intven M, van Vulpen M, Verkooijen HM, Reerink O, Radiother Oncol. 2014, 113, 1–9. - PubMed
-
- Gustavsson B, Carlsson G, Machover D, Petrelli N, Roth A, Schmoll HJ, Tveit KM, Gibson F, Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2015, 14, 1–10; - PubMed
- Engstrom PF, Arnoletti JP, Benson AB 3rd, Chen YJ, Choti MA, Cooper HS, Covey A, Dilawari RA, Early DS, Enzinger PC, Fakih MG, Fleshman J Jr., Fuchs C, Grem JL, Kiel K, Knol JA, Leong LA, Lin E, Mulcahy MF, Rao S, Ryan DP, Saltz L, Shibata D, Skibber JM, Sofocleous C, Thomas J, Venook AP, Willett C, N. National Comprehensive Cancer, J. Natl. Compr. Cancer Netw 2009, 7, 778–831; - PubMed
- Babaei M, Jansen L, Balavarca Y, Sjovall A, Bos A, van de Velde T, Moreau M, Liberale G, Goncalves AF, Bento MJ, Ulrich CM, Schrotz-King P, Lemmens V, Glimelius B, Brenner H, Clin. Colorectal Cancer 2018, 17, e129–e142; - PMC - PubMed
- Beppu N, Yanagi H, Tomita N, J. Anus Rectum Colon 2017, 1, 65–73; - PMC - PubMed
- Ma X, Lee C, Zhang T, Cai J, Wang H, Jiang F, Wu Z, Xie J, Jiang G, Li Z, J. nanobiotechnology 2021, 19, 1–10; - PMC - PubMed
- Bai L, Jiang F, Wang R, Lee C, Wang H, Zhang W, Jiang W, Li D, Ji B, Li Z, J. nanobiotechnology 2020, 18, 1–10; - PMC - PubMed
- Jin J, Zhao Q, J. nanobiotechnology 2020, 18, 1–17. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Restivo A, Delrio P, Deidda S, Spolverato G, Rega D, Cerci M, Barina A, Perin A, Pace U, Zorcolo L, Pucciarelli S, Oncol. Res. Treat 2020, 43, 146–152. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

