MultiR-Net: A Novel Joint Learning Network for COVID-19 segmentation and classification
- PMID: 35305504
- PMCID: PMC8912982
- DOI: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105340
MultiR-Net: A Novel Joint Learning Network for COVID-19 segmentation and classification
Abstract
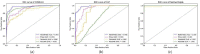
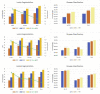
The outbreak of COVID-19 has caused a severe shortage of healthcare resources. Ground Glass Opacity (GGO) and consolidation of chest CT scans have been an essential basis for imaging diagnosis since 2020. The similarity of imaging features between COVID-19 and other pneumonia makes it challenging to distinguish between them and affects radiologists' diagnosis. Recently, deep learning in COVID-19 has been mainly divided into disease classification and lesion segmentation, yet little work has focused on the feature correlation between the two tasks. To address these issues, in this study, we propose MultiR-Net, a 3D deep learning model for combined COVID-19 classification and lesion segmentation, to achieve real-time and interpretable COVID-19 chest CT diagnosis. Precisely, the proposed network consists of two subnets: a multi-scale feature fusion UNet-like subnet for lesion segmentation and a classification subnet for disease diagnosis. The features between the two subnets are fused by the reverse attention mechanism and the iterable training strategy. Meanwhile, we proposed a loss function to enhance the interaction between the two subnets. Individual metrics can not wholly reflect network effectiveness. Thus we quantify the segmentation results with various evaluation metrics such as average surface distance, volume Dice, and test on the dataset. We employ a dataset containing 275 3D CT scans for classifying COVID-19, Community-acquired Pneumonia (CAP), and healthy people and segmented lesions in pneumonia patients. We split the dataset into 70% and 30% for training and testing. Extensive experiments showed that our multi-task model framework obtained an average recall of 93.323%, an average precision of 94.005% on the classification test set, and a 69.95% Volume Dice score on the segmentation test set of our dataset.
Keywords: COVID-19; Interpretability; Multi-scale; Multi-task learning; V-Net.
Copyright © 2022 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we have no financial and personal relationships with other people or organizations that can inappropriately influence our work, there is no professional or other personal interest of any nature or kind in any product, service and/or company that could be construed as influencing the position presented in, or the review of, the manuscript entitled, “MultiR-Net: A Novel Joint Learning Network for COVID-19 Segmentation and classification”.
Figures






Similar articles
-
HFCF-Net: A hybrid-feature cross fusion network for COVID-19 lesion segmentation from CT volumetric images.Med Phys. 2022 Jun;49(6):3797-3815. doi: 10.1002/mp.15600. Epub 2022 Mar 30. Med Phys. 2022. PMID: 35301729 Free PMC article.
-
Joint Learning of 3D Lesion Segmentation and Classification for Explainable COVID-19 Diagnosis.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2021 Sep;40(9):2463-2476. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2021.3079709. Epub 2021 Aug 31. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2021. PMID: 33983881 Free PMC article.
-
Human-in-the-Loop-A Deep Learning Strategy in Combination with a Patient-Specific Gaussian Mixture Model Leads to the Fast Characterization of Volumetric Ground-Glass Opacity and Consolidation in the Computed Tomography Scans of COVID-19 Patients.J Clin Med. 2024 Sep 4;13(17):5231. doi: 10.3390/jcm13175231. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39274444 Free PMC article.
-
GACDN: generative adversarial feature completion and diagnosis network for COVID-19.BMC Med Imaging. 2021 Oct 21;21(1):154. doi: 10.1186/s12880-021-00681-6. BMC Med Imaging. 2021. PMID: 34674660 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CD-Net: Cascaded 3D Dilated convolutional neural network for pneumonia lesion segmentation.Comput Biol Med. 2024 May;173:108311. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2024.108311. Epub 2024 Mar 16. Comput Biol Med. 2024. PMID: 38513395 Review.
Cited by
-
[Hepatocellular carcinoma segmentation and pathological differentiation degree prediction method based on multi-task learning].Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2023 Feb 25;40(1):60-69. doi: 10.7507/1001-5515.202208045. Sheng Wu Yi Xue Gong Cheng Xue Za Zhi. 2023. PMID: 36854549 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
A Systematic Review on Deep Structured Learning for COVID-19 Screening Using Chest CT from 2020 to 2022.Healthcare (Basel). 2023 Aug 24;11(17):2388. doi: 10.3390/healthcare11172388. Healthcare (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37685422 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DuDoCFNet: Dual-Domain Coarse-to-Fine Progressive Network for Simultaneous Denoising, Limited-View Reconstruction, and Attenuation Correction of Cardiac SPECT.IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2024 Sep;43(9):3110-3125. doi: 10.1109/TMI.2024.3385650. Epub 2024 Sep 4. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2024. PMID: 38578853 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 ground-glass opacity segmentation based on fuzzy c-means clustering and improved random walk algorithm.Biomed Signal Process Control. 2023 Jan;79:104159. doi: 10.1016/j.bspc.2022.104159. Epub 2022 Sep 12. Biomed Signal Process Control. 2023. PMID: 36119901 Free PMC article.
-
A novel approach for COVID-19 Infection forecasting based on multi-source deep transfer learning.Comput Biol Med. 2022 Oct;149:105915. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2022.105915. Epub 2022 Aug 5. Comput Biol Med. 2022. PMID: 36063688 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

