Obacunone alleviates ferroptosis during lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by upregulating Nrf2-dependent antioxidant responses
- PMID: 35305560
- PMCID: PMC8933916
- DOI: 10.1186/s11658-022-00318-8
Obacunone alleviates ferroptosis during lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury by upregulating Nrf2-dependent antioxidant responses
Abstract
Background: Acute lung injury (ALI) has received considerable attention in the field of intensive care as it is associated with a high mortality rate. Obacunone (OB), widely found in citrus fruits, is a natural bioactive compound with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant activities. However, it is not clear whether OB protects against lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced ALI. Therefore, in this study, we aimed to evaluate the protective effects of OB and the potential mechanisms against LPS-induced ALI and BEAS-2B cell injury.
Methods: We established a model of BEAS-2B cell injury and a mouse model of ALI by treating with LPS. Samples of in vitro model were subjected to cell death, Cell Counting Kit-8, and lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release assays. The total number of cells and neutrophils, protein content, and levels of IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-1β were determined in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF). Glutathione, reactive oxygen species, and malondialdehyde levels were determined in lung tissue. Additionally, immunohistochemical analysis, immunofluorescence, western blot, quantitative real-time PCR, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay were conducted to examine the effects of OB. Furthermore, mice were treated with an Nrf2 inhibitor (ML385) to verify its role in ferroptosis. Data were analyzed using one-way analysis of variance or paired t-tests.
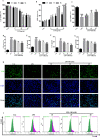
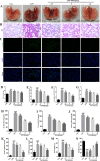
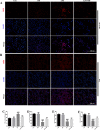
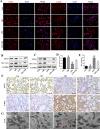
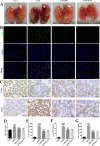
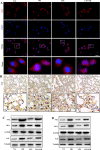
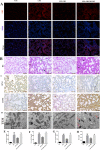
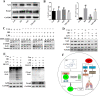
Results: Compared with the LPS group, OB effectively alleviated LPS-induced ALI by decreasing lung wet/dry weight ratio, reactive oxygen species and malondialdehyde production, and superoxide dismutase and glutathione consumption in vivo. In addition, OB significantly alleviated lung histopathological injury, reduced inflammatory cytokine secretion and Fe2+ and 4-HNE levels, and upregulated GPX4, SLC7A11, and Nrf2 expression. Mechanistically, OB activated Nrf2 by inhibiting Nrf2 ubiquitinated proteasome degradation. ML385 reversed the protective effects of OB against LPS-induced ALI.
Conclusion: Overall, OB alleviates LPS-induced ALI, making it a potential novel protective agent against LPS-induced ALI.
Keywords: Acute lung injury; Ferroptosis; Lipopolysaccharide; Nrf2; Obacunone.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Fan E, Brodie D, Slutsky AS. Acute respiratory distress syndrome: advances in diagnosis and treatment. JAMA. 2018;319:698–710. - PubMed
-
- Bae HB, Li M, Kim JP, Kim SJ, Jeong CW, Lee HG, et al. The effect of epigallocatechin gallate on lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury in a murine model. Inflammation. 2010;33:82–91. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

