Detection and characterization of simvastatin and its metabolites in rat tissues and biological fluids using MALDI high resolution mass spectrometry approach
- PMID: 35306510
- PMCID: PMC8934354
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-022-08804-x
Detection and characterization of simvastatin and its metabolites in rat tissues and biological fluids using MALDI high resolution mass spectrometry approach
Abstract
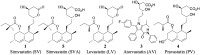
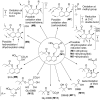
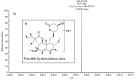
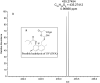
Simvastatin (SV) is a hypolipidemic agent, and it is the 2nd most widely prescribed lipid-lowering drug. Here, the detection and characterization of SV and its metabolites was studied in selected organs/tissues (lung, liver, brain, heart and kidney) and biological samples (blood, urine and feces) of rats. MALDI Orbitrap MS was used as a high-resolution mass analyzer. 2,5-Dihydroxybenzoic acid (DHB) and 1,5-diaminonaphthalene (DAN) were used as matrices. Several sample loading methods onto the MALDI plate were attempted and dried droplet method was found to be superior. Two different cell disruption methods, pulverization and homogenization, were also evaluated for the optimum sensitivity in MALDI. Pulverization allowed the detection of more metabolites in all organs except the liver, where homogenization led to the detection of more metabolites. Altogether, 13 metabolites were detected, and one metabolite tentatively identified as a reduced product is being reported for the first time. SV and its metabolites were distributed to all the tissues studied except the brain. Overall, the results implied that the pulverized samples were more uniform and larger in surface area, resulting in their more efficient and complete extraction during sample preparation. As shown in the present study, MALDI Orbitrap MS is a useful tool to study drug and metabolite detection and characterization.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Distribution study of atorvastatin and its metabolites in rat tissues using combined information from UHPLC/MS and MALDI-Orbitrap-MS imaging.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014 Jul;406(19):4601-10. doi: 10.1007/s00216-014-7880-y. Epub 2014 May 20. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2014. PMID: 24842405
-
Utility of imaging mass spectrometry (IMS) by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization (MALDI) on an ion trap mass spectrometer in the analysis of drugs and metabolites in biological tissues.J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2007 May-Jun;55(3):279-88. doi: 10.1016/j.vascn.2006.11.004. Epub 2006 Dec 5. J Pharmacol Toxicol Methods. 2007. PMID: 17222568
-
An auxiliary matrix for routine analysis of small molecules and biological macromolecules using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization mass spectrometry.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019 Feb;411(5):1041-1052. doi: 10.1007/s00216-018-1532-6. Epub 2019 Jan 7. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2019. PMID: 30613842
-
Ionic (liquid) matrices for matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry-applications and perspectives.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2006 Sep;386(1):24-37. doi: 10.1007/s00216-006-0600-5. Epub 2006 Jul 8. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2006. PMID: 16830111 Review.
-
Biomarker Characterization by MALDI-TOF/MS.Adv Clin Chem. 2015;69:209-54. doi: 10.1016/bs.acc.2015.01.001. Epub 2015 Feb 17. Adv Clin Chem. 2015. PMID: 25934363 Review.
Cited by
-
Development of an LC-MS method for the determination of simvastatin and its hydroxy acid form in muscle tissue and method application.PLoS One. 2025 May 5;20(5):e0322808. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0322808. eCollection 2025. PLoS One. 2025. PMID: 40323990 Free PMC article.
-
LC-MS/MS analysis of carcinogenic tobacco-specific nitrosamines in Spodoptera litura using the QuEChERS method.Sci Rep. 2023 Jul 27;13(1):12151. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-37656-2. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37500666 Free PMC article.
-
XenoMet: A Corpus of Texts to Extract Data on Metabolites of Xenobiotics.ACS Omega. 2025 Jan 12;10(3):2459-2471. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.4c05723. eCollection 2025 Jan 28. ACS Omega. 2025. PMID: 39895765 Free PMC article.
-
Simvastatin is delivered to the brain by high-strength intranasal cationic SMEDDS and nanoemulsions.Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025 Aug;15(8):2749-2764. doi: 10.1007/s13346-024-01769-6. Epub 2025 Jan 2. Drug Deliv Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 39747745
References
-
- Paul A. Drug distribution. In: Raj GM, Raveendran R, editors. Introduction to Basics of Pharmacology and Toxicology: Volume 1: General and Molecular Pharmacology: Principles of Drug Action. Singapore: Springer; 2019.
-
- Gillette JR. The importance of tissue distribution in pharmacokinetics. J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm. 1973;1:497–520. doi: 10.1007/BF01059788. - DOI
-
- Baca QJ, Golan DE. Pharmaconinetics. In: Golan DE, Armstrong EJ, Armstrong AW, editors. Principles of Pharmacology: The pathophysiologic basis of drug therapy. 4. Wolters Kluwer; 2017. pp. 27–42.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

