Infection fatality rate of COVID-19 in community-dwelling elderly populations
- PMID: 35306604
- PMCID: PMC8934243
- DOI: 10.1007/s10654-022-00853-w
Infection fatality rate of COVID-19 in community-dwelling elderly populations
Abstract
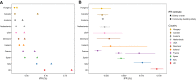
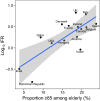
This mixed design synthesis aimed to estimate the infection fatality rate (IFR) of Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in community-dwelling elderly populations and other age groups from seroprevalence studies. Protocol: https://osf.io/47cgb . Eligible were seroprevalence studies done in 2020 and identified by any of four existing systematic reviews; with ≥ 500 participants aged ≥ 70 years; presenting seroprevalence in elderly people; aimed to generate samples reflecting the general population; and whose location had available data on cumulative COVID-19 deaths in elderly (primary cutoff ≥ 70 years; ≥ 65 or ≥ 60 also eligible). We extracted the most fully adjusted (if unavailable, unadjusted) seroprevalence estimates; age- and residence-stratified cumulative COVID-19 deaths (until 1 week after the seroprevalence sampling midpoint) from official reports; and population statistics, to calculate IFRs adjusted for test performance. Sample size-weighted IFRs were estimated for countries with multiple estimates. Thirteen seroprevalence surveys representing 11 high-income countries were included in the main analysis. Median IFR in community-dwelling elderly and elderly overall was 2.9% (range 1.8-9.7%) and 4.5% (range 2.5-16.7%) without accounting for seroreversion (2.2% and 4.0%, respectively, accounting for 5% monthly seroreversion). Multiple sensitivity analyses yielded similar results. IFR was higher with larger proportions of people > 85 years. The IFR of COVID-19 in community-dwelling elderly is lower than previously reported.
Keywords: COVID-19; Elderly; Infection fatality rate.
© 2022. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have completed the ICMJE uniform disclosure form at
Figures
References
-
- Comas-Herrera A, Zalakaín J, Lemmon E, Henderson D, Litwin C, Hsu A, et al. Mortality associated with COVID-19 in care homes: international evidence. Article in LTCcovid.org, International Long-Term Care Policy Network, CPEC-LSE. 14 October2020.
-
- Levin AT, Hanage WP, Owusu-Boaitey N, Cochran KB, Walsh SP, Meyerowitz-Katz G. Assessing the age specificity of infection fatality rates for COVID-19: systematic review, meta-analysis, and public policy implications. Eur J Epidemiol. 2020;35(12):1123–1138. doi: 10.1007/s10654-020-00698-1. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- O’Driscoll M, Dos Santos GR, Wang L, Cummings DAT, Azman AS, Paireau J, et al. Age-specific mortality and immunity patterns of SARS-CoV-2. Nature. 2021;590:140–5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

