Brain Targeting, Antioxidant Polymeric Nanoparticles for Stroke Drug Delivery and Therapy
- PMID: 35306743
- PMCID: PMC9167795
- DOI: 10.1002/smll.202107126
Brain Targeting, Antioxidant Polymeric Nanoparticles for Stroke Drug Delivery and Therapy
Abstract
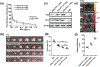
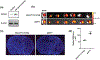
Ischemic stroke is a leading cause of death and disability and remains without effective treatment options. Improved treatment of stroke requires efficient delivery of multimodal therapy to ischemic brain tissue with high specificity. Here, this article reports the development of multifunctional polymeric nanoparticles (NPs) for both stroke treatment and drug delivery. The NPs are synthesized using an reactive oxygen species (ROS)-reactive poly (2,2'-thiodiethylene 3,3'-thiodipropionate) (PTT) polymer and engineered for brain penetration through both thrombin-triggered shrinkability and AMD3100-mediated targeted delivery. It is found that the resulting AMD3100-conjugated, shrinkable PTT NPs, or ASPTT NPs, efficiently accumulate in the ischemic brain tissue after intravenous administration and function as antioxidant agents for effective stroke treatment. This work shows ASPTT NPs are capable of efficient encapsulation and delivery of glyburide to achieve anti-edema and antioxidant combination therapy, resulting in therapeutic benefits significantly greater than those by either the NPs or glyburide alone. Due to their high efficiency in brain penetration and excellent antioxidant bioactivity, ASPTT NPs have the potential to be utilized to deliver various therapeutic agents to the brain for effective stroke treatment.
Keywords: anti-edema; antioxidants; blood-brain barrier; shrinkable nanoparticles; stroke.
© 2022 Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

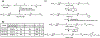
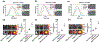
References
-
- Luo T, Wang J, Hao S, Guo T, Ren P, Cheng Z, Gao F, Gong Y, Wang B, Curr. Pharm. Des 2017, 23, 2258. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

