Blocking EGFR with nimotuzumab: a novel strategy for COVID-19 treatment
- PMID: 35306855
- PMCID: PMC8936166
- DOI: 10.2217/imt-2022-0027
Blocking EGFR with nimotuzumab: a novel strategy for COVID-19 treatment
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum.Immunotherapy. 2022 Oct;14(14):1181. doi: 10.2217/imt-2022-0027c1. Immunotherapy. 2022. PMID: 36106709 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Background: Lung injury and STAT1 deficit induce EGFR overexpression in SARS-CoV-2 infection. Patients & methods: A phase I/II trial was done to evaluate the safety and preliminary effect of nimotuzumab, an anti-EGFR antibody, in COVID-19 patients. Patients received from one to three infusions together with other drugs included in the national guideline. Results: 41 patients (31 severe and 10 moderate) received nimotuzumab. The median age was 62 years and the main comorbidities were hypertension, diabetes and cardiovascular disease. The antibody was very safe and the 14-day recovery rate was 82.9%. Inflammatory markers decreased over time. Patients did not show signs of fibrosis. Conclusion: Nimotuzumab is a safe antibody that might reduce inflammation and prevent fibrosis in severe and moderate COVID-19 patients. Clinical Trial Registration: RPCEC00000369 (rpcec.sld.cu).
Keywords: COVID-19; EGFR; SARS-CoV-2; fibrosis; inflammation; monoclonal antibody; nimotuzumab.
Plain language summary
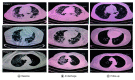
Background: After SARS-CoV-2 infection, many cells in the lung express a new receptor called EGFR. Overexpression of EGFR can worsen the pulmonary disease and provoke fibrosis. Patients & methods: The initial impact of using a drug that blocks EGFR, nimotuzumab, was evaluated in COVID-19 patients. Results: 41 patients received nimotuzumab by the intravenous route together with other medications. The median age was 62 years, and patients had many chronic conditions including hypertension, diabetes and cardiac problems. Treatment was well tolerated and 82.9% of the patients were discharged by day 14. Serial laboratory tests, x-rays and CT scan evaluations showed the improvement of the patients. Conclusion: Nimotuzumab is a safe drug that can be useful to treat COVID-19 patients.
Conflict of interest statement
This study was funded by the Cuban Ministry of Health and the Center of Molecular Immunology. TCR, MRS, DSH, DEI, PLLA, LMP, MTC, AGP and ALAK currently work for the Center of Molecular Immunology, the institution that generated and originally patented nimotuzumab. The authors have no other relevant affiliations or financial involvement with any organization or entity with a financial interest in or financial conflict with the subject matter or materials discussed in the manuscript apart from those disclosed.
No writing assistance was utilized in the production of this manuscript.
Figures

References
-
- Mendelsohn J, Baselga J. Epidermal growth factor receptor targeting in cancer. Semin. Oncol. 33(4), 369–385 (2006). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
