Comparison of Prostate Biopsy Using Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Prostate Biopsy Indications
- PMID: 35307622
- PMCID: PMC9634877
- DOI: 10.5152/eurasianjmed.2022.20349
Comparison of Prostate Biopsy Using Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Patients with Prostate Biopsy Indications
Abstract
Objective: This article aims to evaluate the efficacy of multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging before standard tru-cut biopsy in making prostate cancer diagnosis.
Materials and methods: A total of 160 patients with prostate biopsy indications were prospectively evaluated between May 2017 and October 2018. Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging was taken after obtaining a written informed consent from all patients. Cognitive transrectal ultrasound-guided biopsy was performed based on multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging results. Standard tru-cut biopsy was included to reduce false-negative rate. Statistical analysis was performed using the Statistical Package for Social Sciences version 20.0 software.
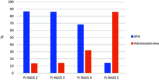
Results: The mean age of the patients was 65.94 ± 7.90 (48-84) years. Around 19.37% of the patients had a specificity in the digital rectal exam. The mean prostate-specific antigen value of the patients with adenocarcinoma was 42.1 ng/mL and it was 10.2 ng/mL in patients with benign prostate hyperplasia. It was observed that the prostate-specific antigen values in prostatic adenocarcinomas were significantly higher than those in benign prostate hyperplasia (P < .001). The results of multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging and the biopsy were 100% similar in terms of zones in patients with adenocarcinoma. All of the biopsy results of the patients who were evaluated to have normal prostate tissue in multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging were evaluated as benign prostate hyperplasia; on the other hand, 13.6% of PI-RADS 2 lesions, 14% of PI-RADS 3 lesions, 31.8% of PI-RADS 4 lesions, and 85.7% of PI-RADS 5 lesions were determined to be adenocarcinoma. It was observed that the prevalence of adenocarcinoma increased as the risk elevated in multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging (P < .001).
Conclusion: Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging evaluated by experienced radiologists may be instructive of urologists and reduce the need for unnecessary biopsies.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous