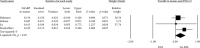Paraoxonase-1 (PON-1) Arylesterase Activity Levels in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease: A Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 35308142
- PMCID: PMC8930235
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4264314
Paraoxonase-1 (PON-1) Arylesterase Activity Levels in Patients with Coronary Artery Disease: A Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Aim: To review and compare the PON-1 arylesterase activity between coronary artery disease (CAD) and non-CAD patients.
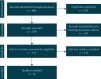
Methods: Data were obtained by searching MEDLINE and Scopus for all investigations published between January 1, 2000 and March 1, 2021 comparing PON-1 arylesterase activity between CAD and controls.
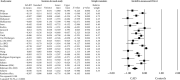
Results: Twenty studies, based on 5417 patients, met the inclusion criteria and were included in the analysis. A random effect model revealed that PON-1 arylesterase activity was significantly lower in the CAD group compared to controls (SMD = -0.587, 95%CI = -0.776 to -0.339, p < 0.0001, I 2 = 92.3%). In CAD patients, the PON-1 arylesterase activity was significantly higher among CAD patients without diabetes mellitus (DM) compared to those with diabetes (SMD: 0.235, 95% CI: 0.014 to 0.456, p = 0.03, I 2 = 0%).
Conclusions: PON-1 activity is significantly lower in CAD patients, and those without DM presented a significantly higher PON-1 arylesterase activity.
Copyright © 2022 Marco Zuin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
References
-
- Misra M. K., Sarwat M., Bhakuni P., Tuteja R., Tuteja N. Oxidative stress and ischemic myocardial syndromes. Medical Science Monitor : International Medical Journal of Experimental and Clinical Research . 2009;15(10):RA209–RA219. - PubMed
-
- Mackness B., Mackness M. I., Arrol S., Turkie W., Durrington P. N. Effect of the human serum paraoxonase 55 and 192 genetic polymorphisms on the protection by high density lipoprotein against low density lipoprotein oxidative modification. FEBS Letters . 1998;423(1):57–60. doi: 10.1016/S0014-5793(98)00064-7. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous