Type 2 Diabetes Complicated With Heart Failure: Research on Therapeutic Mechanism and Potential Drug Development Based on Insulin Signaling Pathway
- PMID: 35308248
- PMCID: PMC8927800
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2022.816588
Type 2 Diabetes Complicated With Heart Failure: Research on Therapeutic Mechanism and Potential Drug Development Based on Insulin Signaling Pathway
Abstract
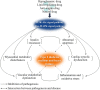
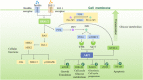
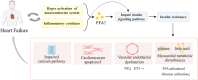
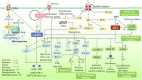
Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and heart failure (HF) are diseases characterized by high morbidity and mortality. They often occur simultaneously and increase the risk of each other. T2DM complicated with HF, as one of the most dangerous disease combinations in modern medicine, is more common in middle-aged and elderly people, making the treatment more difficult. At present, the combination of blood glucose control and anti-heart failure is a common therapy for patients with T2DM complicated with HF, but their effect is not ideal, and many hypoglycemic drugs have the risk of heart failure. Abnormal insulin signaling pathway, as a common pathogenic mechanism in T2DM and HF, could lead to pathological features such as insulin resistance (IR), myocardial energy metabolism disorders, and vascular endothelial disorders. The therapy based on the insulin signaling pathway may become a specific therapeutic target for T2DM patients with HF. Here, we reviewed the mechanisms and potential drugs of insulin signaling pathway in the treatment of T2DM complicated with HF, with a view to opening up a new perspective for the treatment of T2DM patients with HF and the research and development of new drugs.
Keywords: drugs; heart failure; insulin resistance; insulin signaling pathway; myocardial energy metabolism; type 2 diabetes.
Copyright © 2022 Ye, He, Zheng, Wang, Yang, Lin, Xu and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmed R. H., Huri H. Z., Muniandy S., Al-Hamodi Z., Al-Absi B., Alsalahi A., et al. (2017). Altered Circulating Concentrations of Active Glucagon-like Peptide (GLP-1) and Dipeptidyl Peptidase 4 (DPP4) in Obese Subjects and Their Association with Insulin Resistance. Clin. Biochem. 50 (13-14), 746–749. 10.1016/j.clinbiochem.2017.03.008 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

