Virulence Determinants in Staphylococcus aureus Clones Causing Osteomyelitis in Italy
- PMID: 35308345
- PMCID: PMC8927738
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.846167
Virulence Determinants in Staphylococcus aureus Clones Causing Osteomyelitis in Italy
Abstract
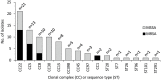
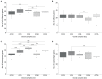
Staphylococcus aureus is the most common pathogen causing osteomyelitis (OM). The aim of this study was to explore the clonal complex (CC) distribution and the pattern of virulence determinants of S. aureus isolates from OM in Italy. Whole-genome sequencing was performed on 83 S. aureus isolates from OM cases in six hospitals. Antibiotic susceptibility tests showed that 30.1% of the isolates were methicillin-resistant S. aureus (MRSA). The most frequent CCs detected were CC22, CC5, CC8, CC30, and CC15, which represent the most common lineages circulating in Italian hospitals. MRSA were limited in the number of lineages (CC22, CC5, CC8, and CC1). Phylogenetic analysis followed the sequence type-CC groupings and revealed a non-uniform distribution of the isolates from the different hospitals. No significant difference in the mean number of virulence genes carried by MRSA or MSSA isolates was observed. Some virulence genes, namely cna, fib, fnbA, coa, lukD, lukE, sak, and tst, were correlated with the CC. However, different categories of virulence factors, such as adhesins, exoenzymes, and toxins, were frequently detected and unevenly distributed among all lineages. Indeed, each lineage carried a variable combination of virulence genes, likely reflecting functional redundancy, and arguing for the importance of those traits for the pathogenicity in OM. In conclusion, no specific genetic trait in the most frequent lineages could explain their high prevalence among OM isolates. Our findings highlight that CCs detected in OM isolates follow the epidemiology of S. aureus infections in the country. It is conceivable that any of the most common S. aureus CC can cause a variety of infections, including OM.
Keywords: Staphylococcus aureus; antibiotic resistance; clones; osteomyelitis; virulence genes; whole genome sequencing.
Copyright © 2022 Pimentel de Araujo, Pirolo, Monaco, Del Grosso, Ambretti, Lombardo, Cassetti, Gargiulo, Riccobono, Visca and Pantosti.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Ahmed S., Meghji S., Williams R. J., Henderson B., Brock J. H., Nair S. P. (2001). Staphylococcus aureus fibronectin binding proteins are essential for internalization by osteoblasts but do not account for differences in intracellular levels of bacteria. Infect. Immun. 69, 2872–2877. doi: 10.1128/IAI.69.5.2872-2877.2001, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bouras D., Doudoulakakis A., Tsolia M., Vaki I., Giormezis N., Petropoulou N., et al. (2018). Staphylococcus aureus osteoarticular infections in children: an 8-year review of molecular microbiology, antibiotic resistance and clinical characteristics. J. Med. Microbiol. 67, 1753–1760. doi: 10.1099/jmm.0.000859, PMID: - DOI - PubMed
-
- Byren I., Bejon P., Atkins B. L., Angus B., Masters S., McLardy-Smith P., et al. (2009). One hundred and twelve infected arthroplasties treated with ‘DAIR’ (debridement, antibiotics and implant retention): antibiotic duration and outcome. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 63, 1264–1271. doi: 10.1093/jac/dkp107, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

