Incidence Trends of Five Common Sexually Transmitted Infections Excluding HIV From 1990 to 2019 at the Global, Regional, and National Levels: Results From the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019
- PMID: 35308518
- PMCID: PMC8924524
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2022.851635
Incidence Trends of Five Common Sexually Transmitted Infections Excluding HIV From 1990 to 2019 at the Global, Regional, and National Levels: Results From the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019
Abstract
Objective: Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are common worldwide and pose a challenge to public health. We conducted this study to assess the annual incidence of five common STIs, including syphilis, chlamydia, gonorrhea, trichomoniasis, and genital herpes at the global, regional, and national levels.
Materials and methods: We obtained detailed data on STIs excluding HIV from 1990 to 2019 from the Global Burden of Disease (GBD) 2019 database. Estimated annual percentage change (EAPC) was calculated to quantify trends in age-standardized incidence rates (ASR) of STIs, stratified by gender, sociodemographic index (SDI) region, and pathogenic microorganism.
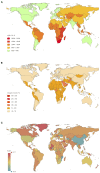
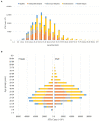
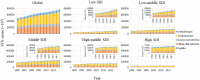
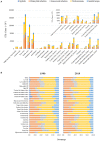
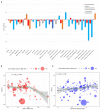
Results: Globally, incident cases of STIs increased by 58.15% from 486.77 million in 1990 to 769.85 million in 2019, but the annual change in ASR was only -0.04% (95% CI -0.09 to 0.01) per year. EAPC was 0.16 (0.06 to 0.26) for syphilis, 0.09 (0.05 to 0.13) for genital herpes, 0.06 (0.03 to 0.09) for trichomoniasis, -0.21 (-0.36 to -0.06) for chlamydia, and -0.14 (-0.19 to -0.08) for gonorrhea. High SDI regions reported significant increases in ASR of syphilis and chlamydia.
Conclusions: The burden of disease from STIs remains large, though control of STIs has contributed to the decreasing incidence in most regions, especially in the low-SDI regions. Globally, over the past 20 years, the ASR has remained stable for trichomoniasis and genital herpes decreased for chlamydia and gonorrhea, and increased for syphilis.
Keywords: STIs; chlamydia; genital herpes; global burden; gonorrhea; syphilis; trichomoniasis.
Copyright © 2022 Fu, Sun, Han, Wang, Xiao, Zhou, Gao, Fitzpatrick, Yuan, Li, Zhan, Lu, Luo, Duan, Hong, Fairley, Zhang, Zhao and Zou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- GBD 2015 Disease and Injury Incidence and Prevalence Collaborators . Global, regional, and national incidence, prevalence, and years lived with disability for 310 diseases and injuries, 1990-2015: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2015. Lancet. (2016) 388:1545–602. 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31678-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) Key facts. (2020). Available online at: http://www.who.int/mediacentre/factsheets/fs110/en/.
-
- Newman L, Rowley J, Vander Hoorn S, Wijesooriya NS, Unemo M, Low N, et al. Global estimates of the prevalence and incidence of four curable sexually transmitted infections in 2012 based on systematic review and global reporting. PLoS One. (2015) 10:e0143304. 10.1371/journal.pone.0143304 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

