Seed-Mediated, Shape-Controlled Synthesis Methods for Platinum-Based Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction-A Mini Review
- PMID: 35308784
- PMCID: PMC8931037
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2022.865214
Seed-Mediated, Shape-Controlled Synthesis Methods for Platinum-Based Electrocatalysts for the Oxygen Reduction Reaction-A Mini Review
Abstract
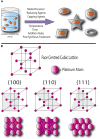
Overcoming the slow oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) kinetics at the cathode of the hydrogen fuel cells requires the use of electrocatalysts containing expensive and scare platinum to achieve reasonable performance, hampering widespread use of the technology due to high material costs and sustainability issues. One option available to tackle this issue is to use new designs to create nanomaterials which achieve excellent electrocatalytic performances and long-lasting stabilities whilst using less platinum than is currently required. Reliably producing nanomaterials with predictable activities and stabilities using simple, safe, and scalable methods is an important research topic to the advancement of fuel cell technologies. The oxygen reduction reaction occurs at the surface of electrocatalytic materials, and since nanomaterial structures exhibit different catalytic activities, their shapes have a strong relationship to the final performance. Seed-mediated synthesis can be used to control the shape of materials with the aim of obtaining products with the most desirable surface properties for the ORR. This review summarized the current advancement of the synthesis of platinum-based ORR and provided the insights for the future development of this field.
Keywords: electrocatalysts; hydrogen fuel cell; oxygen reduction reaction; platinum; seed-mediated; shapecontrolled.
Copyright © 2022 Gray, Munshi, Scowen, Brett and He.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hornberger E., Mastronardi V., Brescia R., Pompa P. P., Klingenhof M., Dionigi F., et al. (2021). Seed-Mediated Synthesis and Catalytic ORR Reactivity of Facet-Stable, Monodisperse Platinum Nano-Octahedra. ACS Appl. Energ. Mater. 4, 9542–9552. 10.1021/acsaem.1c01696 - DOI
-
- Leong G. J., Schulze M. C., Strand M. B., Maloney D., Frisco S. L., Dinh H. N., et al. (2013). Shape-directed Platinum Nanoparticle Synthesis: Nanoscale Design of Novel Catalysts. Appl. Organometal. Chem. 28, 1–17. 10.1002/aoc.3048 - DOI
-
- Leteba G. M., Mitchell D. R. G., Levecque P. B. J., Macheli L., van Steen E., Lang C. I. (2020). High-Index Core-Shell Ni-Pt Nanoparticles as Oxygen Reduction Electrocatalysts. ACS Appl. Nano Mater. 3, 5718–5731. 10.1021/acsanm.0c00915 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

