Integrated autolysis, DNA hydrolysis and precipitation enables an improved bioprocess for Q-Griffithsin, a broad-spectrum antiviral and clinical-stage anti-COVID-19 candidate
- PMID: 35308834
- PMCID: PMC8917701
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bej.2022.108403
Integrated autolysis, DNA hydrolysis and precipitation enables an improved bioprocess for Q-Griffithsin, a broad-spectrum antiviral and clinical-stage anti-COVID-19 candidate
Abstract
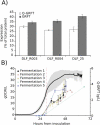
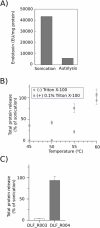
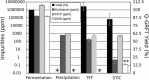
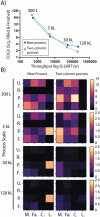
Across the biomanufacturing industry, innovations are needed to improve efficiency and flexibility, especially in the face of challenges such as the COVID-19 pandemic. Here we report an improved bioprocess for Q-Griffithsin, a broad-spectrum antiviral currently in clinical trials for COVID-19. Q-Griffithsin is produced at high titer in E. coli and purified to anticipated clinical grade without conventional chromatography or the need for any fixed downstream equipment. The process is thus both low-cost and highly flexible, facilitating low sales prices and agile modifications of production capacity, two key features for pandemic response. The simplicity of this process is enabled by a novel unit operation that integrates cellular autolysis, autohydrolysis of nucleic acids, and contaminant precipitation, giving essentially complete removal of host cell DNA as well as reducing host cell proteins and endotoxin by 3.6 and 2.4 log10 units, respectively. This unit operation can be performed rapidly and in the fermentation vessel, such that Q-GRFT is obtained with 100% yield and > 99.9% purity immediately after fermentation and requires only a flow-through membrane chromatography step for further contaminant removal. Using this operation or variations of it may enable improved bioprocesses for a range of other high-value proteins in E. coli.
Keywords: Biologics manufacturing; Broad spectrum antiviral; COVID-19; Downstream recovery; Griffithsin.
© 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
JSD, RMM and MDL have financial interests in Roke Biotechnologies, LLC. MDL has a financial interest in DMC Biotechnologies, Inc.
Figures
Update of
-
Integrated Autolysis, DNA Hydrolysis and Precipitation Enables an Improved Bioprocess for Q-Griffithsin, a Broad-Spectrum Antiviral and Clinical-Stage anti-COVID-19 Candidate.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2022 Jan 3:2021.12.30.474602. doi: 10.1101/2021.12.30.474602. bioRxiv. 2022. Update in: Biochem Eng J. 2022 Apr;181:108403. doi: 10.1016/j.bej.2022.108403. PMID: 35018377 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science , Medicine Use and Spending in the U.S: a Review of 2018 and Outlook to 2023, IQVIA Institute for Human Data Science, 2019. 〈https://www.iqvia.com/-/media/iqvia/pdfs/institute-reports/medicine-use-....
-
- Office of the Commissioner, US Food and Drug Administration, Investing in Advanced Manufacturing to Support Public Health, (n.d.). 〈https://www.fda.gov/news-events/fda-voices/investing-advanced-manufactur.... (Accessed 17 December 2021).
-
- Erickson J., Baker J., Barrett S., Brady C., Brower M., Carbonell R., Charlebois T., Coffman J., Connell-Crowley L., Coolbaugh M., Fallon E., Garr E., Gillespie C., Hart R., Haug A., Nyberg G., Phillips M., Pollard D., Qadan M., Ramos I., Rogers K., Schaefer G., Walther J., Lee K. End-to-end collaboration to transform biopharmaceutical development and manufacturing. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2021;118:3302–3312. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Whitford B. Bioprocess intensification: aspirations and achievements. Biotechniques. 2020;69:84–87. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
