Combining metal-metal cooperativity, metal-ligand cooperativity and chemical non-innocence in diiron carbonyl complexes
- PMID: 35308864
- PMCID: PMC8849050
- DOI: 10.1039/d1sc05473b
Combining metal-metal cooperativity, metal-ligand cooperativity and chemical non-innocence in diiron carbonyl complexes
Abstract
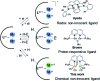
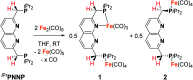
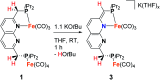
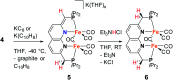
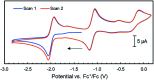
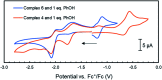
Several metalloenzymes, including [FeFe]-hydrogenase, employ cofactors wherein multiple metal atoms work together with surrounding ligands that mediate heterolytic and concerted proton-electron transfer (CPET) bond activation steps. Herein, we report a new dinucleating PNNP expanded pincer ligand, which can bind two low-valent iron atoms in close proximity to enable metal-metal cooperativity (MMC). In addition, reversible partial dearomatization of the ligand's naphthyridine core enables both heterolytic metal-ligand cooperativity (MLC) and chemical non-innocence through CPET steps. Thermochemical and computational studies show how a change in ligand binding mode can lower the bond dissociation free energy of ligand C(sp3)-H bonds by ∼25 kcal mol-1. H-atom abstraction enabled trapping of an unstable intermediate, which undergoes facile loss of two carbonyl ligands to form an unusual paramagnetic (S = ) complex containing a mixed-valent iron(0)-iron(i) core bound within a partially dearomatized PNNP ligand. Finally, cyclic voltammetry experiments showed that these diiron complexes show catalytic activity for the electrochemical hydrogen evolution reaction. This work presents the first example of a ligand system that enables MMC, heterolytic MLC and chemical non-innocence, thereby providing important insights and opportunities for the development of bimetallic systems that exploit these features to enable new (catalytic) reactivity.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts to declare.
Figures







References
-
- Can M. Armstrong F. A. Ragsdale S. W. Chem. Rev. 2014;114:4149–4174. doi: 10.1021/cr400461p. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Lubitz W. Ogata H. Rüdiger O. Reijerse E. Chem. Rev. 2014;114:4081–4148. doi: 10.1021/cr4005814. - DOI - PubMed
- Wodrich M. D. Hu X. Nat. Rev. Chem. 2017;2:0099. doi: 10.1038/s41570-017-0099. - DOI
- Sippel D. Rohde M. Netzer J. Trncik C. Gies J. Grunau K. Djurdjevic I. Decamps L. Andrade S. L. A. Einsle O. Science. 2018;359:1484–1489. doi: 10.1126/science.aar2765. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Li Y. Rauchfuss T. B. Chem. Rev. 2016;116:7043–7077. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.5b00669. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
- Birrell J. A. Pelmenschikov V. Mishra N. Wang H. Yoda Y. Tamasaku K. Rauchfuss T. B. Cramer S. P. Lubitz W. DeBeer S. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020;142:222–232. doi: 10.1021/jacs.9b09745. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

