BlockIoT: Blockchain-based Health Data Integration using IoT Devices
- PMID: 35308935
- PMCID: PMC8861710
BlockIoT: Blockchain-based Health Data Integration using IoT Devices
Abstract
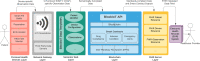
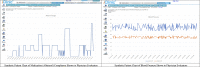
The development and adoption of Electronic Health Records (EHR) and health monitoring Internet of Things (IoT) Devices have enabled digitization of patient records and has also substantially transformed the healthcare delivery system in aspects such as remote patient monitoring, healthcare decision making, and medical research. However, data tends to be fragmented among health infrastructures, and prevents interoperability of medical data at the point of care. In order to address this gap, we introduce BlockIoT that uses blockchain technology to transfer previously inaccessible and centralized data from medical devices to EHR systems, which provides greater insight to providers who can, in turn, provide better outcomes for patients. This notion of interoperability of medical device data is possible through an Application Programming Interface (API), which serves as a versatile endpoint for all incoming medical device data, a distributed file system that ensures data resilience, and knowledge templates that analyze, identify, and represent medical device data to providers. Our participatory design survey on BlockIoT demonstrates that BlockIoT is a suitable system to supplement physicians' clinical practice and increases efficiency in most healthcare specialties, including cardiology, pulmonology, endocrinology, and primary care.
©2021 AMIA - All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Ross Casey. Medical Devices Market Size Worth Around US$ 671.49 Bn by 2027. November 2020.
-
- HIPAA Journal. September 2020 Healthcare Data Breach Report: 9.7 Million Records Compromised, October 2020.
-
- Roter Debra L, Hall Judith A, Merisca Rolande, Nordstrom Beth, Cretin Deborah, Svarstad Bonnie. Effectiveness of interventions to improve patient compliance: a meta-analysis. Medical care. 1998. pp. 1138–1161. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous