Multi-task deep learning-based survival analysis on the prognosis of late AMD using the longitudinal data in AREDS
- PMID: 35308963
- PMCID: PMC8861665
Multi-task deep learning-based survival analysis on the prognosis of late AMD using the longitudinal data in AREDS
Abstract
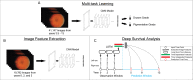
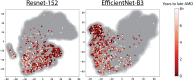
Age-related macular degeneration (AMD) is the leading cause of vision loss. Some patients experience vision loss over a delayed timeframe, others at a rapid pace. Physicians analyze time-of-visit fundus photographs to predict patient risk of developing late-AMD, the most severe form of AMD. Our study hypothesizes that 1) incorporating historical data improves predictive strength of developing late-AMD and 2) state-of-the-art deep-learning techniques extract more predictive image features than clinicians do. We incorporate longitudinal data from the Age-Related Eye Disease Studies and deep-learning extracted image features in survival settings to predict development of late- AMD. To extract image features, we used multi-task learning frameworks to train convolutional neural networks. Our findings show 1) incorporating longitudinal data improves prediction of late-AMD for clinical standard features, but only the current visit is informative when using complex features and 2) "deep-features" are more informative than clinician derived features. We make codes publicly available at https://github.com/bionlplab/AMD_prognosis_amia2021.
©2021 AMIA - All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Congdon Nathan, O’Colmain Benita, Klaver Caroline C. W., Klein Ronald, Mun˜oz Beatriz, Friedman David S., Kempen John, Taylor Hugh R., Mitchell Paul. Eye Diseases Prevalence Research Group. Causes and prevalence of visual impairment among adults in the United States. Archives of ophthalmology (Chicago, Ill. : 1960) April 2004;122(4):477–485. - PubMed
-
- Wong Wan Ling, Su Xinyi, Li Xiang, Cheung Chui Ming G, Klein Ronald, Cheng Ching-Yu, Wong Tien Yin. Global prevalence of age-related macular degeneration and disease burden projection for 2020 and 2040: a systematic review and meta-analysis. The Lancet. Global health. February 2014;2(2):e106–e116. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
