Lipid Analysis of Fracture Hematoma With MALDI-MSI: Specific Lipids are Associated to Bone Fracture Healing Over Time
- PMID: 35309042
- PMCID: PMC8927282
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2021.780626
Lipid Analysis of Fracture Hematoma With MALDI-MSI: Specific Lipids are Associated to Bone Fracture Healing Over Time
Abstract
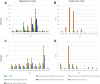
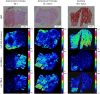
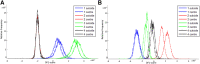
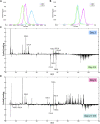
Background: Fracture healing is a complex process, involving cell-cell interactions, various cytokines, and growth factors. Although fracture treatment improved over the last decades, a substantial part of all fractures shows delayed or absent healing. The fracture hematoma (fxh) is known to have a relevant role in this process, while the exact mechanisms by which it influences fracture healing are poorly understood. To improve strategies in fracture treatment, regulatory pathways in fracture healing need to be investigated. Lipids are important molecules in cellular signaling, inflammation, and metabolism, as well as key structural components of the cell. Analysis of the lipid spectrum in fxh may therefore reflect important events during the early healing phase. This study aims to develop a protocol for the determination of lipid signals over time, and the identification of lipids that contribute to these signals, with matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization mass spectrometry imaging (MALDI-MSI) in fxh in healthy fracture healing. Methods: Twelve fxh samples (6 porcine; 6 human) were surgically removed, snap frozen, sectioned, washed, and analyzed using MALDI-MSI in positive and negative ion mode at different time points after fracture (porcine: 72 h; human samples: range 1-19 days). A tissue preparation protocol for lipid analysis in fxh has been developed with both porcine and human fxh. Data were analyzed through principal component- and linear discriminant analyses. Results: A protocol for the preparation of fxh sections was developed and optimized. Although hematoma is a heterogeneous tissue, the intra-variability within fxh was smaller than the inter-variability between fxh. Distinctive m/z values were detected that contributed to the separation of three different fxh age groups: early (1-3 days), middle (6-10 days), and late (12-19 days). Identification of the distinctive m/z values provided a panel of specific lipids that showed a time dependent expression within fxh. Conclusion: This study shows that MALDI-MSI is a suitable analytical tool for lipid analysis in fxh and that lipid patterns within fxh are time-dependent. These lipid patterns within fxh may serve as a future diagnostic tool. These findings warrant further research into fxh analysis using MALDI-MSI and its possible clinical implications in fracture treatment.
Keywords: MALDI-MSI; fracture healing; fracture hematoma; lipids; sample preparation.
Copyright © 2022 Groven, Nauta, Gruisen, Claes, Greven, van Griensven, Poeze, Heeren, Porta Siegel, Cillero-Pastor and Blokhuis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

