Application of berberine-loaded albumin nanoparticles in infections of traumatic wounds
- PMID: 35309105
- PMCID: PMC8918763
Application of berberine-loaded albumin nanoparticles in infections of traumatic wounds
Abstract
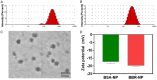
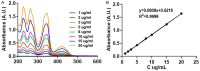
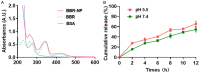
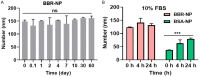
In recent years, the morbidity of infections in traumatic wounds has been on the increase. There are not many kinds of drugs for clinical treatment of infections, and their efficacy and safety are limited. Plant antimicrobial drugs are increasingly popular in mainstream medicine due to the challenges of traditional antibiotics abuse. Berberine has a scavenging effect on infections, however, berberine was restricted from using as a drug preparation with poor stability and bioavailability. Due to the low toxicity of nanoparticles, the green-synthetic, size-controlled approach of nanoparticles has been paid more attention. Therefore, based on the intermolecular disulfide bond network platform built earlier, we designed and developed a strategy to assemble molecular bovine serum albumin into large-sized nanostructures through the reconstructed intermolecular disulfide bond and hydrophobic interaction, and berberine with poor water solubility was encapsulated in it. Nanoassembly with bovine serum albumin increased biostability of berberine and significantly improved its activity against Staphylococcus Aureus (S.aureus) activity, which gives some new insights into the preparation and development of anti-infectives for Chinese medicine.
Keywords: Infections; albumin nanoparticles; berberine; green-synthetic.
IJBT Copyright © 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Combinatorial liposomes of berberine and curcumin inhibit biofilm formation and intracellular methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections and associated inflammation.J Mater Chem B. 2021 Jan 28;9(3):864-875. doi: 10.1039/d0tb02036b. J Mater Chem B. 2021. PMID: 33392614
-
Self-Assembled Nanoparticles of Natural Phytochemicals (Berberine and 3,4,5-Methoxycinnamic Acid) Originated from Traditional Chinese Medicine for Inhibiting Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Curr Drug Deliv. 2021;18(7):914-921. doi: 10.2174/1567201817666201124121918. Curr Drug Deliv. 2021. PMID: 33234104
-
Natural Berberine-Based Chinese Herb Medicine Assembled Nanostructures with Modified Antibacterial Application.ACS Nano. 2019 Jun 25;13(6):6770-6781. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.9b01346. Epub 2019 May 28. ACS Nano. 2019. PMID: 31135129
-
An Updated Review on Therapeutic Potential and Recent Advances in Drug Delivery of Berberine: Current Status and Future Prospect.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2022;23(1):60-71. doi: 10.2174/1389201022666210208152113. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 33557735 Review.
-
Nano strategies for berberine delivery, a natural alkaloid of Berberis.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Aug;104:465-473. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.05.067. Epub 2018 May 25. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29793179 Review.
Cited by
-
Berberine in Sepsis: Effects, Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Strategies.J Immunol Res. 2023 Jan 25;2023:4452414. doi: 10.1155/2023/4452414. eCollection 2023. J Immunol Res. 2023. PMID: 36741234 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Älgå A, Wong S, Shoaib M, Lundgren K, Giske CG, von Schreeb J, Malmstedt J. Infection with high proportion of multidrug-resistant bacteria in conflict-related injuries is associated with poor outcomes and excess resource consumption: a cohort study of Syrian patients treated in Jordan. BMC Infect Dis. 2018;18:233. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
