Peripheral Purinergic Modulation in Pediatric Orofacial Inflammatory Pain Affects Brainstem Nitroxidergic System: A Translational Research
- PMID: 35309172
- PMCID: PMC8933089
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1326885
Peripheral Purinergic Modulation in Pediatric Orofacial Inflammatory Pain Affects Brainstem Nitroxidergic System: A Translational Research
Abstract
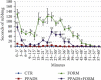
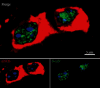
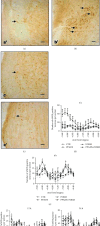
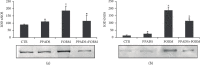
Physiology of orofacial pain pathways embraces primary afferent neurons, pathologic changes in the trigeminal ganglion, brainstem nociceptive neurons, and higher brain function regulating orofacial nociception. The goal of this study was to investigate the nitroxidergic system alteration at brainstem level (spinal trigeminal nucleus), and the role of peripheral P2 purinergic receptors in an experimental mouse model of pediatric inflammatory orofacial pain, to increase knowledge and supply information concerning orofacial pain in children and adolescents, like pediatric dentists and pathologists, as well as oro-maxillo-facial surgeons, may be asked to participate in the treatment of these patients. The experimental animals were treated subcutaneously in the perioral region with pyridoxalphosphate-6-azophenyl-2',4'-disulphonic acid (PPADS), a P2 receptor antagonist, 30 minutes before formalin injection. The pain-related behavior and the nitroxidergic system alterations in the spinal trigeminal nucleus using immunohistochemistry and western blotting analysis have been evaluated. The local administration of PPADS decreased the face-rubbing activity and the expression of both neuronal and inducible nitric oxide (NO) synthase isoforms in the spinal trigeminal nucleus. These results underline a relationship between orofacial inflammatory pain and nitroxidergic system in the spinal trigeminal nucleus and suggest a role of peripheral P2 receptors in trigeminal pain transmission influencing NO production at central level. In this way, orofacial pain physiology should be elucidated and applied to clinical practice in the future.
Copyright © 2022 Elisa Borsani et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Peripheral purinergic receptor modulation influences the trigeminal ganglia nitroxidergic system in an experimental murine model of inflammatory orofacial pain.J Neurosci Res. 2010 Sep;88(12):2715-26. doi: 10.1002/jnr.22420. J Neurosci Res. 2010. PMID: 20648657
-
A potent and selective calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP) receptor antagonist, MK-8825, inhibits responses to nociceptive trigeminal activation: Role of CGRP in orofacial pain.Exp Neurol. 2015 Sep;271:95-103. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.05.005. Epub 2015 May 14. Exp Neurol. 2015. PMID: 25981890
-
Acid-sensing ion channels in trigeminal ganglion neurons innervating the orofacial region contribute to orofacial inflammatory pain.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016 Feb;43(2):193-202. doi: 10.1111/1440-1681.12510. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26510178
-
The Trigeminal Sensory System and Orofacial Pain.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 21;25(20):11306. doi: 10.3390/ijms252011306. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39457088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plastic changes in nociceptive pathways contributing to persistent orofacial pain.J Oral Biosci. 2022 Sep;64(3):263-270. doi: 10.1016/j.job.2022.07.001. Epub 2022 Jul 14. J Oral Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35840073 Review.
Cited by
-
Cardiometabolic Changes in Sirtuin1-Heterozygous Mice on High-Fat Diet and Melatonin Supplementation.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 10;25(2):860. doi: 10.3390/ijms25020860. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38255934 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Neurotrophins in Orofacial Pain Modulation: A Review of the Latest Discoveries.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 4;24(15):12438. doi: 10.3390/ijms241512438. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37569811 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Donaldson M. A targeted approach for managing" "nociceptive orofacial pain. The Compendium of Continuing Education in Dentistry . 2017;38(5):334–335. - PubMed
-
- Patil S. B., Popali D. D., Bondarde P. A., et al. Comparative evaluation of the effectiveness of different pain-alleviating methods before local anesthetic administration in children of 6 to 12 years of age: a clinical study. International Journal of Clinical Pediatric Dentistry . 2021;14(4):447–453. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10005-1998. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Verghese M. W., Kneisler T. B., Boucheron J. A. P2U agonists induce chemotaxis and actin polymerization in human neutrophils and differentiated HL60 cells. The Journal of Biological Chemistry . 1996;271(26):15597–15601. - PubMed
-
- Park W., Masuda I., Cardenal-Escarcena A., Palmer D. L., McCarty D. J. Inorganic pyrophosphate generation from adenosine triphosphate by cell-free human synovial fluid. The Journal of Rheumatology . 1996;23(4):665–671. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

