A Prospective Six-month Single-blind Study Evaluating Changes in Hair Growth and Quality Using a Nutraceutical Supplement in Men and Women of Diverse Ethnicities
- PMID: 35309272
- PMCID: PMC8903234
A Prospective Six-month Single-blind Study Evaluating Changes in Hair Growth and Quality Using a Nutraceutical Supplement in Men and Women of Diverse Ethnicities
Abstract
Objective: The goal of this study was to assess the perceived efficacy of a standardized nutraceutical to improve hair growth and quality in men and women of various ethnicities with self-perceived hair thinning.
Methods: This prospective, single-blind study enrolled healthy men aged 20 to 55 years (n=47) and premenopausal women aged 20 to 45 years (n=51) with self-perceived, mild-to-moderate hair thinning and included African American, Asian, Hispanic Caucasian and Non-Hispanic Caucasian participants. The nutraceutical supplement (Nutrafol® Men or Women Capsules, Nutraceutical Wellness Inc., New York, New York) was taken daily for six months. Subjects were evaluated in the clinic at baseline and Weeks 12 and 24 with two self-assessments at Weeks 4 and 8. Study endpoints were standardized digital imaging and investigator rated assessments. Self-assessment questionnaires rated hair growth, hair satisfaction, and lifestyle factors.
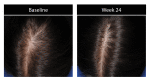
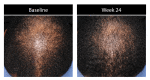
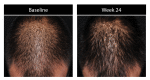
Results: Investigator ratings for baseline hair growth, coverage, density, and volume were significant at Weeks 12 and 24 for all subjects (for each, p<0.001). These significant improvements were seen in 83.7 percent of men and 79.5 percent of women at Week 24. Results were similar across ethnic subgroups with significant benefit at Weeks 12 and 24 (for each, p<0.05). All subjects reported significant improvements in baseline hair appearance/quality, volume/fullness, scalp coverage, thickness, and shedding at Weeks 4, 8, 12 and 24 (for each, p<0.01).
Conclusion: A standardized nutraceutical supplement improved visible hair growth with less notable shedding based on subjects' and investigators' overall perception of treatment benefit for men and women of various ethnic backgrounds.
Keywords: Nutraceutical supplement; ethnicity; hair thinning; men; race; women.
Copyright © 2022. Matrix Medical Communications. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
DISCLOSURES: Ms. Berkowitz and Drs. Marshall, Kogan, and Raymond are employees of Nutraceutical Wellness, LLC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of a Nutraceutical Supplement With Standardized Botanicals in Males With Thinning Hair.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025 Jan;24(1):e16778. doi: 10.1111/jocd.16778. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 39757794 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
A Six-Month, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study Evaluating the Safety and Efficacy of a Nutraceutical Supplement for Promoting Hair Growth in Women With Self-Perceived Thinning Hair.J Drugs Dermatol. 2018 May 1;17(5):558-565. J Drugs Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 29742189 Clinical Trial.
-
A Prospective, Multi-Center Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of a Vegan Nutraceutical to Improve Hair Growth and Quality in Females Following a Plant-Based Diet.J Drugs Dermatol. 2024 Aug 1;23(8):661-668. doi: 10.36849/JDD.8421. J Drugs Dermatol. 2024. PMID: 39093662 Clinical Trial.
-
The Safety and Efficacy of a Sustainable Marine Extract for the Treatment of Thinning Hair: A Summary of New Clinical Research and Results from a Panel Discussion on the Problem of Thinning Hair and Current Treatments.J Drugs Dermatol. 2015 Sep;14(9):s15-22. J Drugs Dermatol. 2015. PMID: 26355631 Review.
-
Growing evidence of the beneficial effects of a marine protein-based dietary supplement for treating hair loss.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2018 Apr;17(2):209-213. doi: 10.1111/jocd.12400. Epub 2017 Sep 16. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2018. PMID: 28921826 Review.
Cited by
-
A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study to Evaluate the Safety and Efficacy of a Nutraceutical Supplement With Standardized Botanicals in Males With Thinning Hair.J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025 Jan;24(1):e16778. doi: 10.1111/jocd.16778. J Cosmet Dermatol. 2025. PMID: 39757794 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Characterization of the role of Facebook groups for patients who use scalp cooling therapy: a survey study.Support Care Cancer. 2024 May 15;32(6):351. doi: 10.1007/s00520-024-08534-y. Support Care Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38748328 Free PMC article.
-
Androgenetic Alopecia: Therapy Update.Drugs. 2023 Jun;83(8):701-715. doi: 10.1007/s40265-023-01880-x. Epub 2023 May 11. Drugs. 2023. PMID: 37166619 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Do Non-Prescription Products Help in Managing Androgenic Alopecia?Skin Appendage Disord. 2025 Jun;11(3):270-281. doi: 10.1159/000542880. Epub 2024 Dec 6. Skin Appendage Disord. 2025. PMID: 40475103 Review.
References
-
- Phillips TG, Slomiany WP, Allison R. Hair loss: common causes and treatment. Am Fam Physician. 2017;96:371–8. - PubMed
-
- Sadick NS, Callender VD, Kircik LH, Kogan S. New Insight Into the Pathophysiology of Hair Loss Trigger a Paradigm Shift in the Treatment Approach. J Drugs Dermatol. 2017;16(11):s135–s40. - PubMed
-
- Farris PK, Rogers N, McMichael A, Kogan S. A Novel Multi-Targeting Approach to Treating Hair Loss, Using Standardized Nutraceuticals. Journal of drugs in dermatology : JDD. 2017;16(11):s141–s8. - PubMed
-
- Ablon G, Kogan S. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of a nutraceutical supplement for promoting hair growth in perimenopausal, menopausal, and postmenopausal women with thinning hair. J Drugs Dermatol. 2021;20:55–61. - PubMed
-
- Ablon G, Kogan S. A Six-Month, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study Evaluating the Safety and Efficacy of a Nutraceutical Supplement for Promoting Hair Growth in Women With Self-Perceived Thinning Hair. Journal of drugs in dermatology : JDD. 2018;17(5):558–65. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources