Association of the Microbiota and Pancreatic Cancer: Opportunities and Limitations
- PMID: 35309293
- PMCID: PMC8928443
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.844401
Association of the Microbiota and Pancreatic Cancer: Opportunities and Limitations
Abstract
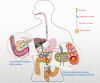
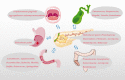
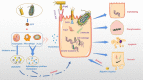
The human body is thoroughly colonized by a wide variety of microorganisms, termed microbiota. Pancreatic cancer, one of the most aggressive forms of cancer, is no exception. The microbiota of pancreatic cancer largely influences and even dominates the occurrence, development and outcome of pancreatic cancer in many ways. Studies have shown that microbiota could change the malignant phenotype and prognosis of pancreatic cancer by stimulating persistent inflammation, regulating the antitumor immune system, changing the tumor microenvironment and affecting cellular metabolism. This is why the association of the microbiota with pancreatic cancer is an emerging area of research that warrants further exploration. Herein, we investigated the potential microbial markers of pancreatic cancer, related research models, the mechanism of action of microbiota in pancreatic cancer, and pancreatic cancer-microbiota-related treatment.
Keywords: biomarkers; microbiota; molecular mechanism; pancreatic cancer; targeted therapy.
Copyright © 2022 Chen, Zhang, Dong, Xu and Zhou.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, Lillemoe KD, Sohn TA, Campbell KA, Sauter PK, et al. Pancreaticoduodenectomy With or Without Distal Gastrectomy and Extended Retroperitoneal Lymphadenectomy for Periampullary Adenocarcinoma, Part 2: Randomized Controlled Trial Evaluating Survival, Morbidity, and Mortality. Ann Surg (2002) 236:355–66. doi: 10.1097/00000658-200209000-00012 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

