Recurrent Severe Subclinical Mastitis and the Risk of HIV Transmission Through Breastfeeding
- PMID: 35309352
- PMCID: PMC8931278
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.822076
Recurrent Severe Subclinical Mastitis and the Risk of HIV Transmission Through Breastfeeding
Abstract
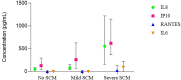
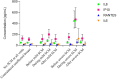
Subclinical mastitis (SCM) is an important risk factor of postnatal HIV-1 transmission that is still poorly understood. A longitudinal sub-study of the ANRS12174 trial including 270 breastfeeding mothers in Lusaka, Zambia measured sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+) in archived paired breast milk samples collected at week 14, 26 and 38 postpartum to determine cumulative incidence of SCM and the effects of recurrent severe SCM on HIV-1 shedding in breast milk. A nested retrospective cohort study including 112 mothers was also done to determine longitudinal effects of SCM on four pro-inflammatory cytokines; IL6, IL8, IP10 and RANTES. The cumulative incidence for any SCM (Na + /K + ratio > 0.6) and severe SCM (Na + /K + ratio > 1) were 58.6% (95%CI: 52.7 - 64.5) and 27.8% (95%CI: 22.5 - 33.1), respectively. In majority of affected mothers (51.4%) severe SCM was recurrent. Both breasts were involved in 11.1%, 33.3% and 70% of the mothers with a single episode, 2 and 3 episodes respectively. In affected breasts, an episode of severe SCM resulted in steep upregulation of the four cytokines considered (IL8, IP10, RANTES and IL6) compared to: before and after the episode; contralateral unaffected breasts; and SCM negative control mothers. Recurrent severe SCM significantly increased the odds of shedding cell-free HIV-1 in breast milk (OR: 5.2; 95%CI: 1.7 - 15.6) whereas single episode of severe SCM did not (OR: 1.8; 95%CI: 0.8 - 4.2). A Na+/K+ ratio > 1 indicative of severe SCM is an excellent indicator of breast inflammation characterized by a steep, localized and temporal upregulation of several pro-inflammatory cytokines that favor HIV-1 shedding in mature breast milk and may facilitate postnatal HIV-1 transmission through breastfeeding.
Keywords: HIV-1 shedding; HIV-1 transmission; breastfeeding; cytokine; inflammation.
Copyright © 2022 Rutagwera, Molès, Kankasa, Mwiya, Tuaillon, Peries, Nagot, Van de Perre and Tylleskär.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization . Mastitis: Causes and Management. Geneva: World Health Organization; (2000).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical