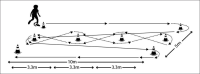
Reliability and validity of a modified Illinois change-of-direction test with ball dribbling speed in young soccer players
- PMID: 35309542
- PMCID: PMC8919884
- DOI: 10.5114/biolsport.2022.104917
Reliability and validity of a modified Illinois change-of-direction test with ball dribbling speed in young soccer players
Abstract
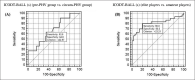
The purpose of this study was to assess test-retest reliability, discriminative and criterion-related validity of the modified Illinois change-of-direction (CoD) test with ball dribbling-speed (ICODT-BALL) in young soccer players of different biological maturity and playing levels. Sixty-five young male soccer players (11.4 ± 1.2 years) participated in this study. The participants were classified according to their biological maturity (pre- and circumpeak height velocity [PHV]) and playing-level (elite and amateur players). During the test-retest time period of two weeks, the following tests were performed during week one and as retest during week two: ICODT-BALL, ICODT, 4 × 9-m shuttle-run, countermovement-jump, triple-hop-test, maximum-voluntary isometric-contraction of back-extensors, Stork, Y-Balance, 10 and 30-m sprints. The ICODT-BALL showed excellent relative (r = 0.995, p < 0.001; ICC = 0.993) and absolute (SEM < 5%; SEM < SWCs(0.2, 0.6, 1.2)) reliability. The circum-PHV (22.8 ± 1.7-s) and elite (22.5 ± 0.9-s) players showed better ICODT-BALL performance than their pre-PHV (24.2 ± 2.5-s) and amateur (25.1 ± 2.8-s) counterparts (p = 0.028 and p < 0.001, respectively). The ICODT-BALL showed "very good" (AUC = 0.81) discriminant validity when comparing the elite and amateur players, and "moderate" (AUC = 0.67) discriminant validity when compared to pre-PHV and circum-PHV boys. ICODT-BALL demonstrated "large" positive associations with the ICODT (r = 0.65; 41.8% shared-variance) and sprint tests (r ≥ 0.52; 27.3 to 34.8% shared-variance). In addition, results showed "moderate" negative associations between ICODT-BALL and strength, and power measures, as well as a "small" negative relationship with balance tests. In conclusion, the ICODT-BALL is a valid and reliable test to evaluate the ability to quickly change directions while ball dribbling in young soccer players. Therefore, practitioners can use the ICODT-BALL as a tool for talent identification.
Keywords: Biological maturity; Football-specific testing; Playing level; Sensitivity; Youth.
Copyright © Biology of Sport 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
This research did not received any financial support. All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript. The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hachana Y, Chaabene H, Nabli MA, Attia A, Moualhi J, Farhat N, et al. Test-retest reliability, criterion-related validity, and minimal detectable change of the Illinois agility test in male team sport athletes. J Strength Cond Res. 2013;27(10):2752–9. - PubMed
-
- Brughelli M, Cronin J, Levin G, Chaouachi A. Understanding change of direction ability in sport: a review of resistance training studies. Sports Med. 2008;38(12):1045–63. - PubMed
-
- Mujika I, Santisteban J, Impellizzeri FM, Castagna C. Fitness determinants of success in men’s and women’s football. J Sports Sci. 2009;27(2):107–14. - PubMed
-
- Sheppard JM, Young WB. Agility literature review: classifications, training and testing. J Sports Sci. 2006;24(9):919–32. - PubMed
-
- Jeffreys I, Huggins S, Davies N. Delivering a gamespeed-focused speed and agility development program in an English Premier League soccer academy. Strength Cond J. 2018;40(3):23–32.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources