The Collagen Receptor Discoidin Domain Receptor 1b Enhances Integrin β1-Mediated Cell Migration by Interacting With Talin and Promoting Rac1 Activation
- PMID: 35309920
- PMCID: PMC8928223
- DOI: 10.3389/fcell.2022.836797
The Collagen Receptor Discoidin Domain Receptor 1b Enhances Integrin β1-Mediated Cell Migration by Interacting With Talin and Promoting Rac1 Activation
Abstract
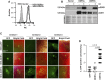
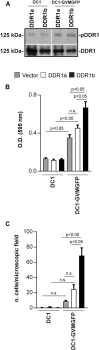
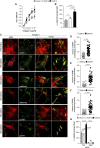
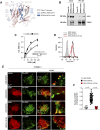
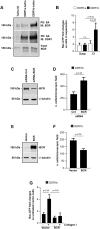
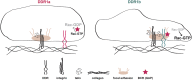
Integrins and discoidin domain receptors (DDRs) 1 and 2 promote cell adhesion and migration on both fibrillar and non fibrillar collagens. Collagen I contains DDR and integrin selective binding motifs; however, the relative contribution of these two receptors in regulating cell migration is unclear. DDR1 has five isoforms (DDR1a-e), with most cells expressing the DDR1a and DDR1b isoforms. We show that human embryonic kidney 293 cells expressing DDR1b migrate more than DDR1a expressing cells on DDR selective substrata as well as on collagen I in vitro. In addition, DDR1b expressing cells show increased lung colonization after tail vein injection in nude mice. DDR1a and DDR1b differ from each other by an extra 37 amino acids in the DDR1b cytoplasmic domain. Interestingly, these 37 amino acids contain an NPxY motif which is a central control module within the cytoplasmic domain of β integrins and acts by binding scaffold proteins, including talin. Using purified recombinant DDR1 cytoplasmic tail proteins, we show that DDR1b directly binds talin with higher affinity than DDR1a. In cells, DDR1b, but not DDR1a, colocalizes with talin and integrin β1 to focal adhesions and enhances integrin β1-mediated cell migration. Moreover, we show that DDR1b promotes cell migration by enhancing Rac1 activation. Mechanistically DDR1b interacts with the GTPase-activating protein (GAP) Breakpoint cluster region protein (BCR) thus reducing its GAP activity and enhancing Rac activation. Our study identifies DDR1b as a major driver of cell migration and talin and BCR as key players in the interplay between integrins and DDR1b in regulating cell migration.
Keywords: Rac1; extracellular matrix; integrins; migration; receptor activation; receptor tyrosine kinase.
Copyright © 2022 Borza, Bolas, Zhang, Browning Monroe, Zhang, Meiler, Skwark, Harris, Lapierre, Goldenring, Hook, Rivera, Brown, Leitinger, Tyska, Moser, Böttcher, Zent and Pozzi.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alves F., Vogel W., Mossie K., Millauer B., Höfler H., Ullrich A. (1995). Distinct Structural Characteristics of Discoidin I Subfamily Receptor Tyrosine Kinases and Complementary Expression in Human Cancer. Oncogene 10, 609–618. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

