Study on the Prediction Method of Long-term Benign and Malignant Pulmonary Lesions Based on LSTM
- PMID: 35309999
- PMCID: PMC8924408
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.791424
Study on the Prediction Method of Long-term Benign and Malignant Pulmonary Lesions Based on LSTM
Abstract
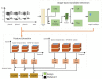
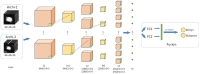
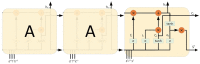
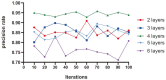
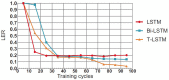
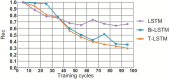
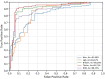
In order to more accurately and comprehensively characterize the changes and development rules of lesion characteristics in pulmonary medical images in different periods, the study was conducted to predict the evolution of pulmonary nodules in the longitudinal dimension of time, and a benign and malignant prediction model of pulmonary lesions in different periods was constructed under multiscale three-dimensional (3D) feature fusion. According to the sequence of computed tomography (CT) images of patients at different stages, 3D interpolation was conducted to generate 3D lung CT images. The 3D features of different size lesions in the lungs were extracted using 3D convolutional neural networks for fusion features. A time-modulated long short-term memory was constructed to predict the benign and malignant lesions by using the improved time-length memory method to learn the feature vectors of lung lesions with temporal and spatial characteristics in different periods. The experiment shows that the area under the curve of the proposed method is 92.71%, which is higher than that of the traditional method.
Keywords: 3D CNNs; characteristics of the fusion; multiscale three-dimensional feature; prediction; pulmonary lesions; time-modulated LSTM.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Wang and Aftab.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Aaron R., Miller J. B., Christin N., Jeffrey C. (2018). Neuroscience Learning from Longitudinal Cohort Studies of Alzheimer’s Disease: Lessons for Disease-Modifying Drug Programs and an Introduction to the center for Neurodegeneration and Translational Neuroscience. New York, NY: Alzheimers & Dementia Translational Research & Clinical Interventions. S2352873718300350–. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baytas I. M., Xiao C., Zhang X., Wang F., Zhou J. (2017). “Patient Subtyping via Time-Aware Lstm Networks,” in The 23rd ACM SIGKDD International Conference. 10.1145/3097983.3097997 - DOI
-
- Bodla N., Zheng J., Xu H., Chen J. C., Chellappa R. (2017). “Deep Heterogeneous Feature Fusion for Template-Based Face Recognition,” in 2017 IEEE Winter Conference on Applications of Computer Vision (WACV). 10.1109/WACV.2017.71 - DOI
-
- Boudjemaa R., Ouaar F., Oliva D. (2020). Fractional Lévy Flight Bat Algorithm for Global Optimisation. Ijbic 15 (2), 100–112. 10.1504/ijbic.2020.10028011 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

