Oxycodone Alleviates Endometrial Injury via the TLR4/NF- κ B Pathway
- PMID: 35310024
- PMCID: PMC8933090
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/6153279
Oxycodone Alleviates Endometrial Injury via the TLR4/NF- κ B Pathway
Abstract
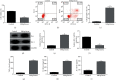
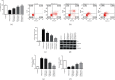
Endometrial injury is a common female disease. This study was designed to illustrate the effects of oxycodone on mifepristone-induced human endometrial stromal cells (hEndoSCs) injury and delineate the underlying molecular mechanism. hEndoSCs were stimulated with mifepristone to generate the endometrial injury in vitro model. hEndoSCs viability, cytotoxicity, and apoptosis were measured by methyl thiazolyl tetrazolium (MTT) assay, lactate dehydrogenase assay (LDH), and flow cytometry (FCM) analysis, respectively. Meanwhile, quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-qPCR) and Western blot assay were conducted to evaluate gene and protein expressions. The secretions of inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6) were measured using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The data revealed that mifepristone exposure memorably inhibited hEndoSCs viability and promoted cell apoptosis and inflammatory cytokines secretion, and oxycodone had no cytotoxicity on hEndoSCs. Oxycodone increased hEndoSCs growth, blocked cell apoptosis, enhanced Bcl-2 expression, reduced Bax levels, and decreased the secretion of inflammatory cytokines in mifepristone-induced hEndoSCs, exhibiting the protective effects in endometrial injury. In addition, the TLR4/NF-κB pathway-related protein levels (TLR4 and p-p65) in mifepristone-treated hEndoSCs were enhanced, while these enhancements were inhibited by oxycodone treatment. In conclusion, oxycodone exhibited the protective role in mifepristone-triggered endometrial injury via inhibiting the TLR4/NF-κB signal pathway.
Copyright © 2022 Aibing Zhu and Jianping Yang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
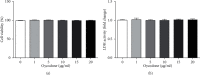
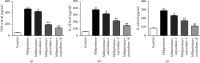
Similar articles
-
Oxycodone alleviates mifepristone-stimulated human endometrial stromal cell injury by activating the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023 Sep;11(9):e1008. doi: 10.1002/iid3.1008. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023. PMID: 37773689 Free PMC article.
-
Exosomes Derived from Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Mifepristone-Induced Human Endometrial Stromal Cell Injury.Stem Cells Int. 2020 Jan 25;2020:6091269. doi: 10.1155/2020/6091269. eCollection 2020. Stem Cells Int. 2020. PMID: 32399046 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of miR-7 on Hcy-induced rat cerebral arterial vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, migration and inflammatory factor expression by targeting MMP-14 to regulate TLR4/NF-κB signaling pathway.Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2020 Oct 31;66(7):12-17. Cell Mol Biol (Noisy-le-grand). 2020. PMID: 33287916
-
Inhibition of NF-κB by Pyrrolidine Dithiocarbamate Prevents the Inflammatory Response in a Ligature-Induced Peri-Implantitis Model: A Canine Study.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;49(2):610-625. doi: 10.1159/000492997. Epub 2018 Aug 30. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 30165363
-
Heparin alleviates LPS-induced endothelial injury by regulating the TLR4/MyD88 signaling pathway.Exp Ther Med. 2021 Dec;22(6):1397. doi: 10.3892/etm.2021.10833. Epub 2021 Oct 1. Exp Ther Med. 2021. PMID: 34650645 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Oxycodone alleviates mifepristone-stimulated human endometrial stromal cell injury by activating the Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023 Sep;11(9):e1008. doi: 10.1002/iid3.1008. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2023. PMID: 37773689 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guney M., Oral B., Demirin H., Karahan N., Mungan T., Delibas N. Protective effects of vitamins C and E against endometrial damage and oxidative stress in fluoride intoxication. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology . 2007;34(5-6):467–474. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2007.04596.x. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

