Nature against Diabetic Retinopathy: A Review on Antiangiogenic, Antioxidant, and Anti-Inflammatory Phytochemicals
- PMID: 35310030
- PMCID: PMC8926515
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/4708527
Nature against Diabetic Retinopathy: A Review on Antiangiogenic, Antioxidant, and Anti-Inflammatory Phytochemicals
Abstract
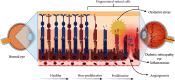
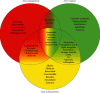
Background and Purpose. Diabetes mellitus (DM), hyperglycemia, and hypertension can result in diabetic retinopathy (DR), which is a major cause of blindness on a global scale. Development of DR is associated with decreased endothelial cells, increased basal membrane thickness, permeation of the retinal blood barrier, and neovascularization in patients. The purpose of the present review is to provide an overview of the findings regarding applications of phytochemicals for DR treatment and could be a beneficial resource for further clinical studies and also a basis for pharmaceutical purposes for drug design. Materials and Methods. A narrative literature review was performed from electronic databases including Web of Science, PubMed, and Scopus to analyze the effects of different phytochemicals to prevent or treat oxidation, angiogenesis, and inflammation in diabetic retinopathy. The inclusion criteria were original studies, which included the effects of different phytochemicals on diabetic retinopathy. The exclusion criteria included studies other than original articles, studies which assessed the effects of phytochemicals on nondiabetic retinopathy, and studies which used phytochemical-rich extracts. Results and Conclusions. Studies have shown that increased levels of inflammatory cytokines, angiogenic, and oxidative stress factors are involved in the progression and pathogenesis of DR. Therefore, phytochemicals with their anti-inflammatory, antiangiogenic, and antioxidant properties can prevent DR progression and retinal damage through various cellular mechanisms. It is also shown that some phytochemicals can simultaneously affect the inflammation, oxidation, and angiogenesis in DR.
Copyright © 2022 Mohammad Amin Khazeei Tabari et al.
Conflict of interest statement
All the authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The ginger extract could improve diabetic retinopathy by inhibiting the expression of e/iNOS and G6PDH, apoptosis, inflammation, and angiogenesis.J Food Biochem. 2022 May;46(5):e14084. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.14084. Epub 2022 Jan 20. J Food Biochem. 2022. PMID: 35060143
-
Angiogenic and antiangiogenic factors in proliferative diabetic retinopathy.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2006 Feb;2(1):71-98. doi: 10.2174/157339906775473671. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2006. PMID: 18220619 Review.
-
Beneficial effects of phytochemicals in diabetic retinopathy: experimental and clinical evidence.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017 Jun;21(11):2769-2783. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28678306 Review.
-
Prognostic factors for the development and progression of proliferative diabetic retinopathy in people with diabetic retinopathy.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023 Feb 22;2(2):CD013775. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013775.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2023. PMID: 36815723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical observations and mechanistic insights of traditional Chinese medicine in the management of diabetic retinopathy.Pharm Biol. 2024 Dec;62(1):529-543. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2024.2369292. Epub 2024 Jun 26. Pharm Biol. 2024. PMID: 38921697 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the Molecular Underpinnings of Skin Regeneration and Wound Healing: The Role of Renin Angiotensin.Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2024 Jul-Sep;16(3):146-155. doi: 10.18502/ajmb.v16i3.15740. Avicenna J Med Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 39132629 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unlocking the Potential: How Flavonoids Affect Angiogenesis, Oxidative Stress, Inflammation, Proliferation, Invasion, and Alter Receptor Interactions in Endometriosis.Food Sci Nutr. 2024 Dec 7;13(1):e4607. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.4607. eCollection 2025 Jan. Food Sci Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39803270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Patient Adherence for Oral Combination Therapies in Diabetes Management: A Scoping Review.Health Sci Rep. 2025 Apr 29;8(5):e70780. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.70780. eCollection 2025 May. Health Sci Rep. 2025. PMID: 40309616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The signaling pathways of traditional Chinese medicine in treating diabetic retinopathy.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Jun 19;14:1165649. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1165649. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37405050 Free PMC article. Review.
-
β-Asarone Alleviates High-Glucose-Induced Oxidative Damage via Inhibition of ROS Generation and Inactivation of the NF-κB/NLRP3 Inflammasome Pathway in Human Retinal Pigment Epithelial Cells.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Jul 11;12(7):1410. doi: 10.3390/antiox12071410. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37507949 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Mehrabadi M. E., Salemi Z., Babaie S., Panahi M. Effect of biochanin A on retina levels of vascular endothelial growth factor, tumor necrosis factor-alpha and interleukin-1beta in rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Canadian Journal of Diabetes . 2018;42(6):639–644. doi: 10.1016/j.jcjd.2018.03.008. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources