LuQi Formula Ameliorates Myocardial Fibrosis by Suppressing TLR4/MyD88/NF- κ B Pathway and NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Mice with Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 35310035
- PMCID: PMC8933100
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/5867987
LuQi Formula Ameliorates Myocardial Fibrosis by Suppressing TLR4/MyD88/NF- κ B Pathway and NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation in Mice with Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
Background: Myocardial fibrosis caused by myocardial infarction (MI) is the key factor leading to cardiac remodeling; nod-like receptor family pyrin domain-containing 3 (NLRP3) plays an important role in regulation of myocardial injury; however, its relationship with TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway is largely unreported. In recent years, traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases has shown its unique advantages and broad application prospects. LuQi Formula (LQF) has been used for more than 20 years in Shuguang Hospital (Shanghai, China), and it was confirmed that it can improve the clinical symptoms of patients after MI. Here, we investigated the mechanism of LQF by suppressing NLRP3 inflammasome activation and TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB pathway in mice with MI.
Purpose: The purpose of this study was to verify the positive effects of the LQF in ameliorating myocardial fibrosis and inflammasome infiltration in the MI mice in vivo.
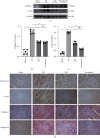
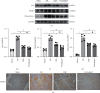
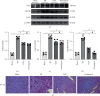
Methods: Forty mice were randomized into four groups: the sham group, the MI group, the LQF group, and the perindopril group (n = 10 per group). Left anterior descending (LAD) coronary artery ligation was performed in all groups except the sham group. The mice were treated with LQF after MI. After 4 weeks, LDH, cTnI, IL-1β, and IL-18 were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kit, and cardiac function was evaluated by echocardiography. Hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) and Masson staining were used to evaluate the myocardial injury and fibrosis. Western blot was used to evaluate the expression of collagen I, α-SMA, NLRP3 inflammasome, and TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. Immunohistochemical analysis was used to further detect the expression of Fibronectin, α-SMA, collagen I, collagen III, NLRP3, and NF-κB in myocardial tissue.
Results: Compared with the MI group, the ejection fraction (EF) and fractional shortening (FS) in the LQF group were significantly improved, while the left ventricular end diastolic diameter (LVEDd) and left ventricular internal dimension systole (LVIDs) were significantly decreased. The representative staining of H&E and Masson showed that treatment with LQF could effectively reduce myocardial injury and fibrosis. ELISA results showed that serum LDH, cTnI, TNF-α, IL-18, and IL-1β in LQF group were significantly lower than those in MI group. The western blot results showed that the expressions of collagen I and α-SMA were decreased significantly in the LQF group. Moreover, the expressions of NLRP3 inflammasome and TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway were downregulated in the LQF treatment group.
Conclusion: Our results suggested that LQF could significantly improve cardiac function and ameliorate myocardial fibrosis. In addition, we found that LQF could downregulate the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway and then inhibit the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome, suggesting that LQF alleviated cardiac fibrosis by decreasing the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway and then inhibited NLRP3 inflammasome activation in MI mice, which indicates potential therapeutic effect of LQF on patients with MI.
Copyright © 2022 Xiaoqing Zhang et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
LuQi Formula Regulates NLRP3 Inflammasome to Relieve Myocardial-Infarction-Induced Cardiac Remodeling in Mice.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021 Jun 28;2021:5518083. doi: 10.1155/2021/5518083. eCollection 2021. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2021. PMID: 34257682 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the TLR4/Myd88/NF-κB Signaling Pathway on NLRP3 Inflammasome in Coronary Microembolization-Induced Myocardial Injury.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;47(4):1497-1508. doi: 10.1159/000490866. Epub 2018 Jun 21. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29940584
-
The stems of Syringa oblata Lindl. exert cardioprotective effects against acute myocardial ischemia by inhibiting the TLR4/MyD88/NF-κB and NLRP3 inflammasome signaling pathways in mice.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Mar 26;344:119563. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2025.119563. Epub 2025 Feb 25. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 40015537
-
Targeting the Inflammasome in Cardiovascular Disease.JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2021 Nov 3;7(1):84-98. doi: 10.1016/j.jacbts.2021.08.006. eCollection 2022 Jan. JACC Basic Transl Sci. 2021. PMID: 35128212 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Mechanism of NLRP3 inflammasome intervention for synovitis in knee osteoarthritis: A review of TCM intervention.Front Genet. 2023 Mar 29;14:1159167. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1159167. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37065495 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Active ingredients of traditional Chinese medicine inhibit NOD-like receptor protein 3 inflammasome: a novel strategy for preventing and treating heart failure.Front Immunol. 2025 Jan 24;16:1520482. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1520482. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 39925805 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ruddox V., Sandven I., Munkhaugen J., Skattebu J., Edvardsen T., Otterstad J. E. Atrial fibrillation and the risk for myocardial infarction, all-cause mortality and heart failure: A systematic review and meta-analysis. European Journal of Preventive Cardiology . 2017;24(14):1555–1566. - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

