Quercetin Beneficial Role in the Homeostatic Variation of Certain Trace Elements in Dyslipidemic Mice
- PMID: 35310037
- PMCID: PMC8933091
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/3299505
Quercetin Beneficial Role in the Homeostatic Variation of Certain Trace Elements in Dyslipidemic Mice
Abstract
Background: Quercetin's role in the homeostasis of certain trace elements in dyslipidemia induced in mice was assessed.
Methods: Forty BALB/c mice were allocated into 4 groups as follows: control; HFD, received fat diet; HFD + Q group, received HFD +500 mg/L quercetin; and blank control (Q)-normal food + 500 mg/L quercetin in drinking water.
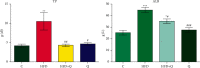
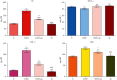
Results: By analyzing the values of total proteins, albumins, cholesterol, triglycerides, HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, and the levels of several trace elements in blood and organs, we perceived a statistically significant increase ( ∗∗ , p < 0.01) of TP, ALB, TC, TGE, and LDL-c. A nonsignificant decrease was ascertained to HDL-c value in the HFD and quercetin groups (p > 0.05). In the HFD group, all analyzed elements in the kidney and spleen increased, also Cu, Li, Mg, Mn, Pb, and of B, Ba, Cr, Cd, Cu, Fe, Li, Mn, Ni, Pb, and Zn in the heart increased, but furthermore, Ag, B, Ba, Cd, Cr, Fe, Ni, and Zn in blood, Ag and Zn in the liver, and Cd in the spleen decreased. In the HFD group who received quercetin, elements (except B) were decreased in kidney and liver, also increased Ag, Ba, Cr, Fe, Li, Ni, Zn in blood, but similarly, Ag, B, Ba, Cd, Cu, Mn, and Pb declined in the spleen and heart.
Conclusions: Results proved the quercetin beneficial role.
Copyright © 2022 Florin Muselin et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Jayarama N., Lakshmaiah M. R. Prevalence and pattern of dyslipidemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus patients in a rural tertiary care centre, southern India. Global Journal of Medicine and Public Health . 2012;1:24–27.
-
- Snehalatha C., Nanditha A., Shetty A. S., Ramachandran A. Hypertriglyceridaemia either in isolation or in combination with abdominal obesity is strongly associated with atherogenic dyslipidaemia in Asian Indians. Diabetes Research and Clinical Practice . 2011;94(1):140–145. doi: 10.1016/j.diabres.2011.07.016. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

