Preventive Potential of the Aqueous Extract of the Mixture of Bidens pilosa (Asteraceae) and Cymbopogon citratus (Poaceae) Aerial Parts on Hypertension Induced by a Chronic Salt and Alcohol Consumption on the Rats
- PMID: 35310038
- PMCID: PMC8926541
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/1980622
Preventive Potential of the Aqueous Extract of the Mixture of Bidens pilosa (Asteraceae) and Cymbopogon citratus (Poaceae) Aerial Parts on Hypertension Induced by a Chronic Salt and Alcohol Consumption on the Rats
Abstract
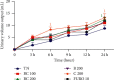
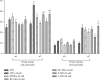
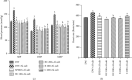
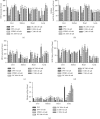
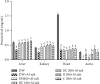
High blood pressure (HBP) is currently one of the main risk factors for cardiovascular and kidney diseases. Nowadays, populations make extensive use of alternative medicine for their health problems. Bidens pilosa (B. pilosa) and Cymbopogon citratus (C. citratus) are used individually in the traditional treatment of cardiovascular disorders. This study assessed the effects of the mixture of these two plants aqueous extract on HBP in rats. Male rats (42) were divided into 7 groups of 6 rats each. Normotensive rats received only distilled water and formed group 1. The other animals received ethanol + salt preceded by distilled water (10 mL/kg; group 2) and spironolactone (10 mg/kg; group 3); the aqueous extracts of the mixture (100 and 200 mg/kg; groups 4 and 5) isolated plants B. pilosa (200 mg/kg; group 6) and C. citratus (200 mg/kg; group 7). Animals were treated for 7 weeks during which water consumption and urine volume were assessed; then, hemodynamic parameters were recorded, and rats were sacrificed. Serum and some organs (liver, kidney, heart, and aorta) were used to evaluate biochemical parameters. Ingestion of ethanol + salt leads to a significant increase in urinary volume and water intake that were significantly prevented by the extracts from the mixture and isolated plants. Ethanol + salt solution significantly increased the blood pressure, heart rate, triglycerides (TG), total cholesterol (TC), low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (LDL-chol), very-low-density lipoprotein cholesterol (VLDL-chol), atherogenic indices, liver and kidney function parameters, and malondialdehyde (MDA) levels. However, the levels of high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-chol), albumin, reduced glutathione (GSH), catalase, and superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity were significantly reduced. The extracts of the mixture and isolated plants significantly prevented all these variations with a more pronounced action for the lowest dose of the mixture on the lipid profile, oxidative stress, and kidney function. These observations confirm the beneficial effects of B. pilosa and C. citratus to manage hypertension.
Copyright © 2022 Yannick Carlos Tcheutchoua et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Acute and Subchronic Toxicity Studies on the Aqueous Extract of the Plant Mixture (Bidens pilosa and Cymbopogon citratus Aerial Parts) in Rat Model.J Toxicol. 2022 Dec 2;2022:1998433. doi: 10.1155/2022/1998433. eCollection 2022. J Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 36506716 Free PMC article.
-
Antihypertensive potential of the aqueous extract which combine leaf of Persea americana Mill. (Lauraceae), stems and leaf of Cymbopogon citratus (D.C) Stapf. (Poaceae), fruits of Citrus medical L. (Rutaceae) as well as honey in ethanol and sucrose experimental model.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014 Dec 17;14:507. doi: 10.1186/1472-6882-14-507. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 25519078 Free PMC article.
-
Antihypertensive and antioxidant effects of Allanblackia floribunda Oliv. (Clusiaceae) aqueous extract in alcohol- and sucrose-induced hypertensive rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2010 Apr 21;128(3):634-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2010.02.025. Epub 2010 Mar 1. J Ethnopharmacol. 2010. PMID: 20193752
-
Hepatoprotective effect of Cymbopogon citratus aqueous extract against hydrogen peroxide-induced liver injury in male rats.Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2014 Jan 28;11(2):447-51. doi: 10.4314/ajtcam.v11i2.31. eCollection 2014. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2014. PMID: 25435631 Free PMC article.
-
Protective effect of Cymbopogon citratus on hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in the reproductive system of male rats.Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2013 Dec;59(6):329-36. doi: 10.3109/19396368.2013.827268. Epub 2013 Aug 19. Syst Biol Reprod Med. 2013. PMID: 23957393
Cited by
-
Acute and Subchronic Toxicity Studies on the Aqueous Extract of the Plant Mixture (Bidens pilosa and Cymbopogon citratus Aerial Parts) in Rat Model.J Toxicol. 2022 Dec 2;2022:1998433. doi: 10.1155/2022/1998433. eCollection 2022. J Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 36506716 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the Anti-Hypertensive Potential of Lemongrass-A Comprehensive Review.Biology (Basel). 2022 Sep 22;11(10):1382. doi: 10.3390/biology11101382. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Network Pharmacology and Molecular Docking-Based Strategy to Investigate the Multitarget Mechanisms of Shenqi Yizhi Granule on Alzheimer's Disease.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Apr 30;2022:8032036. doi: 10.1155/2022/8032036. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 35535155 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Guindo I. Thèse de doctorat en pharmacie, Faculté de medecine de pharmacie et d’odonto-stomatologie . Mali, Bamako: Université de Bamako; 2006. Etude du traitement traditionnel de l’hypertension artérielle au mali.
-
- Who,” Geneva: World Health Organization, 2021. https://www.who.int/fr/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/hypertension.
-
- WHO. P. mondial de l’hypertension: Un « tueur silencieux » responsable d’une crise de santé publique mondiale . Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization; 2013.
-
- Who. Noncommunicable diseases increase risk of dying from COVID-19 in Africa,” WHO Reg. Off. Afric. 2020.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

