Extracellular matrix gene expression in human trabecular meshwork cells following mechanical fluid flow stimulation
- PMID: 35310043
- PMCID: PMC8907041
- DOI: 10.18240/ijo.2022.03.03
Extracellular matrix gene expression in human trabecular meshwork cells following mechanical fluid flow stimulation
Abstract
Aim: To investigate changes in extracellular matrix (ECM) gene expression in human trabecular meshwork (HTM) cells in response to mechanical fluid flow stimulation.
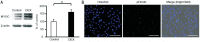
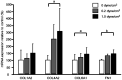
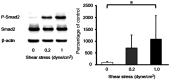
Methods: HTM cells were grown on a glass plate coated with 0.02% type I collagen (COL) and exposed to shear stress (0, 0.2, 1.0 dyne/cm2) for 12h. Changes in genes related to the ECM were evaluated by real-time reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction. Phosphorylation of Smad2 protein was investigated by Western blotting.
Results: After mechanical stimulation, COL type 4 alpha 2, COL type 6 alpha 1, and fibronectin-1 mRNA were significantly higher than the static control (P<0.05, <0.05, and <0.01, respectively). The metalloproteinase-2 and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 mRNA were significantly higher than the static control (P<0.05 and <0.01, respectively), while the differences in the tissue inhibitors of metalloproteinases-2 mRNA were not significant. The phosphorylation of Smad2 levels was significantly higher compared to the static control cells.
Conclusion: Changes in the expressions of genes associated ECM metabolism result in HTM cells after mechanical stimulation. The mechanical stimulation of the aqueous humor to the trabecular meshwork may promote ECM turnover and contribute to intraocular pressure homeostasis.
Keywords: aqueous humor; extracellular matrix; glaucoma; intraocular pressure; shear stress; trabecular meshwork.
International Journal of Ophthalmology Press.
Figures

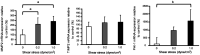
References
-
- Tamm ER. The trabecular meshwork outflow pathways: structural and functional aspects. Exp Eye Res. 2009;88(4):648–655. - PubMed
-
- Costagliola C, dell'Omo R, Agnifili L, Bartollino S, Fea AM, Uva MG, Zeppa L, Mastropasqua L. How many aqueous humor outflow pathways are there? Surv Ophthalmol. 2020;65(2):144–170. - PubMed
-
- Ueda J, Wentz-Hunter K, Yue BYJT. Distribution of myocilin and extracellular matrix components in the juxtacanalicular tissue of human eyes. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 2002;43(4):1068–1076. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
