Successful Management of a Noncommunicating Rudimentary Uterine Horn Pregnancy by Laparoscopic Surgery: A Case Report and Literature Review
- PMID: 35310117
- PMCID: PMC8926057
- DOI: 10.4103/GMIT.GMIT_157_20
Successful Management of a Noncommunicating Rudimentary Uterine Horn Pregnancy by Laparoscopic Surgery: A Case Report and Literature Review
Abstract
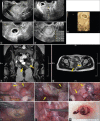
Pregnancy in a noncommunicating rudimentary horn is extremely rare but can cause serious clinical complications, such as uterine rupture. The standard treatment is excision of the rudimentary horn, and recently, in some cases, laparoscopic resection has been performed in the first trimester of gestation. Herein, we present a case of noncommunicating rudimentary horn pregnancy (NCRHP), which was diagnosed by magnetic resonance imaging at 6 weeks of gestation and treated by laparoscopic surgery. However, we have also found some rare cases in which patients could obtain live newborn babies. Since management is affected by the different levels of obstetric medical care and diagnostic tools, we also performed a review and analysis of NCRHP. A PubMed search yielded 103 cases reported in the English literature. Correct diagnosis and laparoscopic treatment were achieved more frequently in developed countries, especially in the first trimester of gestation. On the other hand, symptoms, including abdominal pain and hypovolemic shock, tended to occur in the second trimester of gestation. This period was also found to be a risk factor for uterine rupture. Among 18 patients at the third trimester of gestation, 13 obtained live neonatal infants. Therefore, detailed information about this disease is crucial for proper treatments.
Keywords: Country; gestational age; laparoscopic surgery; noncommunicating rudimentary horn pregnancy; uterine rupture.
Copyright: © 2022 Gynecology and Minimally Invasive Therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Passos IM, Britto RL. Diagnosis and treatment of Müllerian malformations. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2020;59:183–8. - PubMed
-
- O’Leary JL, O’Leary JA. Rudimentary horn pregnancy. Obstet Gynecol. 1963;22:371–5. - PubMed
-
- Reichman D, Laufer MR, Robinson BK. Pregnancy outcomes in unicornuate uteri: A review. Fertil Steril. 2009;91:1886–94. - PubMed
-
- Heinonen PK. Unicornuate uterus and rudimentary horn. Fertil Steril. 1997;68:224–30. - PubMed
-
- Nahum GG. Rudimentary uterine horn pregnancy. The 20th-century worldwide experience of 588 cases. J Reprod Med. 2002;47:151–63. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
