Analyzing the Patient Behavior for Improving the Medical Treatment Using Smart Healthcare and IoT-Based Deep Belief Network
- PMID: 35310183
- PMCID: PMC8930207
- DOI: 10.1155/2022/6389069
Analyzing the Patient Behavior for Improving the Medical Treatment Using Smart Healthcare and IoT-Based Deep Belief Network
Retraction in
-
Retracted: Analyzing the Patient Behavior for Improving the Medical Treatment Using Smart Healthcare and IoT-Based Deep Belief Network.J Healthc Eng. 2023 Aug 9;2023:9806271. doi: 10.1155/2023/9806271. eCollection 2023. J Healthc Eng. 2023. PMID: 37593485 Free PMC article.
Abstract
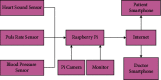
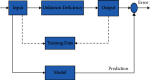
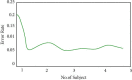
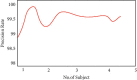
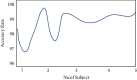
Patient behavioral analysis is a critical component in treating patients with a variety of issues, with head trauma, neurological disease, and mental illness. The analysis of the patient's behavior aids in establishing the disease's core cause. Patient behavioral analysis has a number of contests that are much more problematic in traditional healthcare. With the advancement of smart healthcare, patient behavior may be simply analyzed. A new generation of information technologies, particularly the Internet of Things (IoT), is being utilized to transform the traditional healthcare system in a variety of ways. The Internet of Things (IoT) in healthcare is a crucial role in offering improved medical facilities to people as well as assisting doctors and hospitals. The proposed system comprises of a variety of medical equipment, such as mobile-based apps and sensors, which is useful in collecting and monitoring the medical information and health data of patient and interact to the doctor via network connected devices. This research may provide key information on the impact of smart healthcare and the Internet of Things in patient beavior and treatment. Patient data are exchanged via the Internet, where it is viewed and analyzed using machine learning algorithms. The deep belief neural network evaluates the patient's particulars from health data in order to determine the patient's exact health state. The developed system proved the average error rate of about 0.04 and ensured accuracy about 99% in analyzing the patient behavior.
Copyright © 2022 Rasha M. K. Mohamed et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures




References
-
- Ismail A., Salem M. L., Elkholy A., Elmashad W., Ali G. A. M. In-silico analysis of protein receptors contributing to SARS- COV-2 high infectivity. Information Sciences Letters . 2021;10(3):561–570.
-
- Al-Rawi O. Y. M., Al-Dayyeni W. S., Reda I. COVID-19 impact on education and work in the kingdom of Bahrain: survey study. Information Sciences Letters . 2021;10(3):427–433.
-
- Petrakis E. G. M., Sotiriadis S., Soultanopoulos T., Renta P. T., Buyya R., Bessis N. Internet of things as a service (itaas): challenges and solutions for management of sensor data on the cloud and the fog. Internet of Things . 2018;3-4:156–174. doi: 10.1016/j.iot.2018.09.009. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

