COVID-19 Induced Economic Slowdown and Mental Health Issues
- PMID: 35310204
- PMCID: PMC8931846
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.777350
COVID-19 Induced Economic Slowdown and Mental Health Issues
Abstract
The COVID-19 pandemic has pressed a pause button on global economic development, and induced significant mental health problems. In order to demonstrate the progressed relationship between the pandemic, economic slowdown, and mental health burden, we overviewed the global-level gross domestic product changes and mental problems variation since the outbreak of COVID-19, and reviewed comprehensively the specific sectors influenced by the pandemic, including international trade, worldwide travel, education system, healthcare system, and individual employment. We hope to provide timely evidence to help with the promotion of policymakers' effective strategies in mitigating economic losses induced by the pandemic; we suggest different governments or policy makers in different countries to share information and experience in dealing with COVID-19-induced economic slowdown and promote COVID-19 vaccine popularization plan to protect every individual worldwide against the coronavirus essentially; and we appeal international information share and collaboration to minimize stigmatization related to adverse mental consequences of COVID-19 and to increase mental health wellbeings of people all over the world.
Keywords: COVID-19; GDP; economic slowdown; education system; healthcare system; international trade; mental health issues; unemployment.
Copyright © 2022 Gong, Liu, Zheng, Mei, Que, Yuan, Yan, Shi, Meng, Bao and Lu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
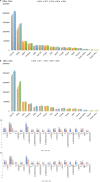
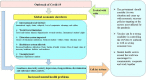
References
-
- Alshekaili M., Hassan W., Al Said N., Al Sulaimani F., Jayapal S. K., Al-Mawali A., et al. (2020). Factors associated with mental health outcomes across healthcare settings in Oman during COVID-19: frontline versus non-frontline healthcare workers. BMJ Open 10:e042030. 10.1136/bmjopen-2020-042030 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- An L., Wynne M. A., Zhang R. (2021). Shock-dependent exchange rate pass-through: evidence based on a narrative sign approach for Japan. J. Int. Money Finance 118:102462. 10.24149/gwp379 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

