Multiple Roles of Grit in the Relationship Between Interpersonal Stress and Psychological Security of College Freshmen
- PMID: 35310215
- PMCID: PMC8929422
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2022.824214
Multiple Roles of Grit in the Relationship Between Interpersonal Stress and Psychological Security of College Freshmen
Abstract
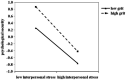
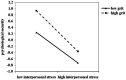
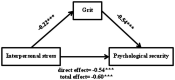
Grit, as an important positive psychological quality, has rarely been studied for its role involved in the mechanism between stress and psychological security. This article explores the moderating and mediating role of grit in the relationship between interpersonal stress and psychological security of freshmen through two studies. In study 1, freshmen from several Chinese universities (N = 1,224) were recruited to complete a battery of questionnaire, including assessments about interpersonal stress, grit, and psychological security. The moderating effect analysis showed that grit moderated the relationship between interpersonal stress and psychological security. Specifically, grit buffered the negative effects of interpersonal stress on freshmen's psychological security, but this effect was obvious only when the level of interpersonal stress was relatively low, and decreased when the level of interpersonal stress was high. In study 2, college freshmen from another university apart from above ones (N = 604) were recruited, and we verified the results of study 1 and further explored the mediating role of grit in the relationship between interpersonal stress and security. The moderating effect analysis of study 2 also verified that of study 1. The mediating effect analysis showed that interpersonal stress not only negatively predicted psychological security, but also affected psychological security through the mediation of grit. In general, grit played a mediating and moderating role in the relationship between interpersonal stress and psychological security. This study provides first-hand evidence to explain the multiple roles of grit in the relationship between interpersonal stress and psychological security.
Keywords: college freshmen; grit; interpersonal stress; multiple roles; psychological security.
Copyright © 2022 Yang, Shi, Tang, Zhu and Xiong.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alan S., Boneva T., Ertac S. (2019). Ever failed, try again, succeed better: results from a randomized educational intervention on grit. Q. J. Econ. 134, 1121–1162. doi: 10.1093/qje/qjz006 - DOI
-
- Bostrom M., Ernsth Bravell M., Lundgren D., Bjorklund A. (2013). Promoting sense of security in old-age care. Health 05, 56–63. doi: 10.4236/health.2013.56A2009 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

