Endophytic Bacterium Serratia plymuthica From Chinese Leek Suppressed Apple Ring Rot on Postharvest Apple Fruit
- PMID: 35310399
- PMCID: PMC8929176
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.802887
Endophytic Bacterium Serratia plymuthica From Chinese Leek Suppressed Apple Ring Rot on Postharvest Apple Fruit
Abstract
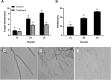
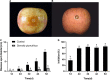
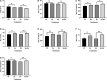
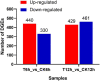
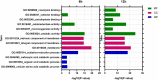
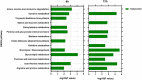
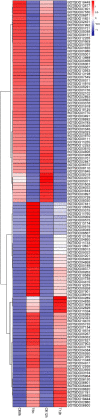
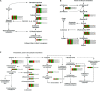
Apple ring rot caused by Botryosphaeria dothidea is an economically significant plant disease that spreads across the apple production areas in China. The pathogen infects apple fruits during the growing season and results in postharvest fruits rot during storage, which brings about a huge loss to plant growers. The study demonstrated that an endophytic bacterium Serratia plymuthica isolated from Chinese leek (Allium tuberosum) significantly suppressed the mycelial growth, severely damaging the typical morphology of B. dothidea, and exerted a high inhibition of 84.64% against apple ring rot on postharvest apple fruit. Furthermore, S. plymuthica significantly reduced the titratable acidity (TA) content, enhanced the soluble sugar (SS) content, vitamin C content, and SS/TA ratio, and maintained the firmness of the fruits. Furthermore, comparing the transcriptomes of the control and the S. plymuthica treated mycelia revealed that S. plymuthica significantly altered the expressions of genes related to membrane (GO:0016020), catalytic activity (GO:0003824), oxidation-reduction process (GO:0055114), and metabolism pathways, including tyrosine metabolism (ko00280), glycolysis/gluconeogenesis (ko00010), and glycerolipid metabolism (ko00561). The present study provided a possible way to control apple ring rot on postharvest fruit and a solid foundation for further exploring the underlying molecular mechanism.
Keywords: Botryosphaeria dothidea; RNA-seq; Serratia plymuthica; biocontrol; fruit quality.
Copyright © 2022 Sun, Liu, Li and Huang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The reviewer PL declared a shared affiliation with the authors to the handling editor at the time of review.
Figures

References
-
- Adam E., Muller H., Erlacher A., Berg G. (2016). Complete genome sequences of the Serratia plymuthica strains 3Rp8 and 3Re4-18, two rhizosphere bacteria with antagonistic activity towards fungal phytopathogens and plant growth promoting abilities. Stand. Genomic Sci. 11:61. 10.1186/s40793-016-0185-3 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bai S., Dong C., Zhu J., Zhang Y., Dai H. (2015). Identification of a xyloglucan-specific endo-(1-4)-beta-D-glucanase inhibitor protein from apple (Malus x domestica Borkh.) as a potential defense gene against Botryosphaeria dothidea. Plant Sci. 231 11–19. 10.1016/j.plantsci.2014.11.003 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

