Trending of a falsely elevated serum creatinine after a pediatric nitromethane ingestion: A case report
- PMID: 35310404
- PMCID: PMC8913454
- DOI: 10.1002/emp2.12689
Trending of a falsely elevated serum creatinine after a pediatric nitromethane ingestion: A case report
Abstract
Introduction: Nitromethane is a primary nitroalkane used as a solvent and a fuel that may be toxic by ingestion, inhalation, or contact. Its presence can be detected in serum of exposed persons, but levels are not readily available to guide patient care. Nitromethane has been shown to falsely elevate serum creatinine when clinical laboratories use Jaffe assays to measure creatinine; enzymatic assays are not affected. Ex vivo experiments have demonstrated a linear relationship between serum nitromethane and the elevation in Jaffe assay creatinine. This case report demonstrates an elevation of creatinine measured by Jaffe assay with normal creatinine measurement by enzymatic assay after exposure to nitromethane.
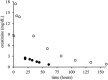
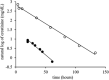
Case report: A 21-month-old girl ingested an unmeasured quantity of a hobby fuel, a fuel containing methanol, nitromethane (20%), and lubricants used in miniature internal combustion engines, such as remote-controlled cars. She was initially evaluated at a community hospital, treated empirically for methanol toxicity with fomepizole and folic acid, and transferred to a university hospital for further management. By 19 hours after ingestion, methanol was below detection, but a serum creatinine of 2.63 mg/dl raised concern for kidney injury. Toxicology consultation recognized that the creatinine had been measured using a Jaffe assay and recommended a repeat creatinine using an enzymatic assay, which was within normal limits. The patient remained an inpatient for further evaluation, which permitted trending of her Jaffe assay creatinine over a 3-day period. The Jaffe assay creatinine demonstrated a gradual decline; repeat enzymatic assay creatinine remained within normal limits.
Discussion: The decline in this pediatric patient's Jaffe assay creatinine is consistent with first-order clearance of nitromethane, which has been previously described in adult exposures. This case demonstrates how Jaffe assay-derived serum creatinine may be useful in the pediatric population to establish, quantify, and trend nitromethane exposure with essential concurrent use of an enzymatic assay to determine actual creatinine.
Keywords: Jaffe assay; creatinine; enzymatic assay; falsely elevated creatinine; ingestion; nitromethane; pediatric.
© 2022 The Authors. JACEP Open published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American College of Emergency Physicians.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Co-ingestion of methanol and nitromethane: using falsely elevated creatinine as indicator for methanol antidote use.Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2007 Jul;8(4):392-3. doi: 10.1097/01.PCC.0000269393.00760.71. Pediatr Crit Care Med. 2007. PMID: 17545934
-
Detection of ingested nitromethane and reliable creatinine assessment using multiple common analytical methods.Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2018 Apr;56(4):237-244. doi: 10.1080/15563650.2017.1360497. Epub 2017 Aug 17. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2018. PMID: 28814126
-
Elevated creatinine after ingestion of model aviation fuel: interference with the Jaffe reaction by nitromethane.J Paediatr Child Health. 1999 Oct;35(5):503-4. doi: 10.1046/j.1440-1754.1999.355402.x. J Paediatr Child Health. 1999. PMID: 10571769
-
Calibration and precision of serum creatinine and plasma cystatin C measurement: impact on the estimation of glomerular filtration rate.J Nephrol. 2014 Oct;27(5):467-75. doi: 10.1007/s40620-014-0087-7. Epub 2014 Apr 8. J Nephrol. 2014. PMID: 24711159 Review.
-
Generation of New Synthons for Synthesis Through Activation of Nitromethane.ChemSusChem. 2024 Oct 7;17(19):e202400454. doi: 10.1002/cssc.202400454. Epub 2024 Jun 5. ChemSusChem. 2024. PMID: 38702899 Review.
Cited by
-
Perfluorooctanesulfonate Can Cause Negative Bias in Creatinine Measurement in Hemodialysis Patients Using Polysulfone Dialysis Membranes.Membranes (Basel). 2022 Aug 13;12(8):778. doi: 10.3390/membranes12080778. Membranes (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36005693 Free PMC article.
References
-
- National Center for Biotechnology Information . PubChem Compound Summary for CID 6375, Nitromethane. Bethesda, MD: National Center for Biotechnology Information; 2020.
-
- National Center for Biotechnology Information . PubChem Annotation Record for NITROMETHANE, Source: Hazardous Substances Data Bank (HSDB). Bethesda, MD: National Center for Biotechnology Information; 2020.
-
- Mullins ME, Hammett‐Stabler CA. Intoxication with nitromethane‐containing fuels: don't be “fueled” by the creatinine. J Toxicol Clin Toxicol. 1998;36(4):315‐320. - PubMed
-
- Murphy CM, Devlin JJ, Beuhler MC, et al. Detection of ingested nitromethane and reliable creatinine assessment using multiple common analytical methods. Clin Toxicol. 2018;56(4):237‐244. - PubMed
-
- Boshoff PE, Gailey K, Moosa MR. Falsely elevated plasma creatinine levels as a marker of nitromethane poisoning. SAMJ. 2008;98(2):97‐98. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
