Two-Year Outcome of Aflibercept Intravitreal Injection in Vitrectomized Eyes with Diabetic Macular Edema
- PMID: 35310546
- PMCID: PMC8923833
- DOI: 10.2147/OPTH.S352152
Two-Year Outcome of Aflibercept Intravitreal Injection in Vitrectomized Eyes with Diabetic Macular Edema
Abstract
Purpose: To evaluate the efficacy of intravitreal aflibercept injection (IAI) for vitrectomized eyes with diabetic macular edema (DME) at two years.
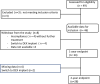
Methods: This is a prospective, non-comparative, multicenter observational study including diabetic patients with visual acuity between 20/400 to 20/40 due to DME, who have undergone vitrectomy at least 3 months before the first aflibercept injection. Treatment protocol included 5 monthly aflibercept injection followed by a ProReNata regimen during the first year. Participants were managed at clinicians' discretion using Treat and Extend or Observe and Plan regimen during the second year. Visual acuity, OCT findings and number of IAI were assessed at two years.
Results: Available data for 28 eyes with DME previously vitrectomized treated with aflibercept intravitreal injection during at least 2 years were collected. Visual gain was +5.4 letters (p = 0.01), and central macular thickness decreased significantly -62µm, p < 0.001) at 2 years. Resolution of macular edema allowing discontinuation of aflibercept was observed in 7 eyes (15%). Mean number of injections was 14.6, and mean interval injection was 6.4 weeks for 2 years.
Conclusion: These results suggest that IAI is beneficial in vitrectomized eyes leading to improvement of visual and anatomical outcome which was maintained for 2 years.
Keywords: aflibercept; anti-VEGF; diabetic macular edema; vitrectomy.
© 2022 Tran et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Prof. Dr. Thi Ha Chau Tran reports grants from Bayer Healthcare, during the conduct of the study. Dr Joel Uzzan reports personal fees from Bayer, Allergan, Novartis, and Horus, outside the submitted work. Prof. Dr. Laurent Kodjikian reports personal fees from AbbVie, Novartis, Bayer, and Roche, outside the submitted work. Dr Ali Erginay reports grants from Allergan, Bayer, and Novartis, during the conduct of the study. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources