Toward Assessing the Functional Connectivity of Spinal Neurons
- PMID: 35310548
- PMCID: PMC8927546
- DOI: 10.3389/fncir.2022.839521
Toward Assessing the Functional Connectivity of Spinal Neurons
Abstract
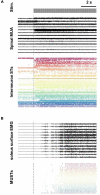
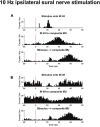
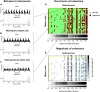
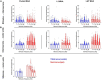
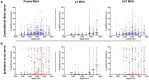
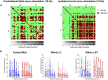
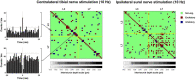
Spinal interneurons play a critical role in motor output. A given interneuron may receive convergent input from several different sensory modalities and descending centers and relay this information to just as many targets. Therefore, there is a critical need to quantify populations of spinal interneurons simultaneously. Here, we quantify the functional connectivity of spinal neurons through the concurrent recording of populations of lumbar interneurons and hindlimb motor units in the in vivo cat model during activation of either the ipsilateral sural nerve or contralateral tibial nerve. Two microelectrode arrays were placed into lamina VII, one at L3 and a second at L6/7, while an electrode array was placed on the surface of the exposed muscle. Stimulation of tibial and sural nerves elicited similar changes in the discharge rate of both interneurons and motor units. However, these same neurons showed highly significant differences in prevalence and magnitude of correlated activity underlying these two forms of afferent drive. Activation of the ipsilateral sural nerve resulted in highly correlated activity, particularly at the caudal array. In contrast, the contralateral tibial nerve resulted in less, but more widespread correlated activity at both arrays. These data suggest that the ipsilateral sural nerve has dense projections onto caudal lumbar spinal neurons, while contralateral tibial nerve has a sparse pattern of projections.
Keywords: high density arrays; interneuron; motoneuron; single units; spinal cord circuitry.
Copyright © 2022 Zaback, Tiwari, Krupka, Marchionne, Negro, Lemay and Thompson.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The handling editor declared a past collaboration with one of the author ML.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Five sources of a dorsal root potential: their interactions and origins in the superficial dorsal horn.J Neurophysiol. 1997 Aug;78(2):860-71. doi: 10.1152/jn.1997.78.2.860. J Neurophysiol. 1997. PMID: 9307119
-
Distribution of oligosynaptic group I input to the cat medial gastrocnemius motoneuron pool.J Neurophysiol. 1985 Feb;53(2):497-517. doi: 10.1152/jn.1985.53.2.497. J Neurophysiol. 1985. PMID: 2984351
-
Differential modulation of primary afferent depolarization of segmental and ascending intraspinal collaterals of single muscle afferents in the cat spinal cord.Exp Brain Res. 2004 Jun;156(3):377-91. doi: 10.1007/s00221-003-1788-7. Epub 2004 Feb 19. Exp Brain Res. 2004. PMID: 14985894
-
Sensory and descending motor circuitry during development and injury.Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2018 Dec;53:156-161. doi: 10.1016/j.conb.2018.08.008. Epub 2018 Sep 8. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 2018. PMID: 30205323 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions between spinal interneurons and ventral spinocerebellar tract neurons.J Physiol. 2013 Nov 15;591(22):5445-51. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2012.248740. Epub 2013 Jan 21. J Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23339177 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Linking cortex and contraction-Integrating models along the corticomuscular pathway.Front Physiol. 2023 May 10;14:1095260. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2023.1095260. eCollection 2023. Front Physiol. 2023. PMID: 37234419 Free PMC article.
-
Myomatrix arrays for high-definition muscle recording.Elife. 2023 Dec 19;12:RP88551. doi: 10.7554/eLife.88551. Elife. 2023. PMID: 38113081 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bannatyne B. A., Edgley S. A., Hammar I., Jankowska E., Maxwell D. J. (2006). Differential projections of excitatory and inhibitory dorsal horn interneurons relaying information from group II muscle afferents in the cat spinal cord. J. Neurosci. 26 2871–2880. 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5172-05.2006 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

