Permanent endoscopic transpapillary gallbladder drainage using a novel spiral stent (IYO-stent)
- PMID: 35310723
- PMCID: PMC8828186
- DOI: 10.1002/deo2.40
Permanent endoscopic transpapillary gallbladder drainage using a novel spiral stent (IYO-stent)
Abstract
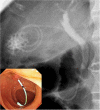
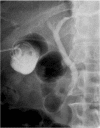
Background and aim: Endoscopic transpapillary gallbladder drainage (ETGBD) is widely performed. However, there is no consensus on the appropriate diameter, length, and shape of the stent that should be used in this procedure. In addition, there are limited data on the outcomes of permanent ETGBD. In our facility, a stent with a novel spiral structure (IYO-stent) is permanently placed in patients with acute cholecystitis who are not indicated for surgery. This study examined the efficacy and safety of the IYO-stent in cases of permanent ETGBD.
Methods: We retrospectively examined patients who underwent permanent ETGBD using the IYO-stent from April 2018 to December 2020.
Results: Eleven patients were included in this study. The technical success and the clinical success rate were 91%. One patient had a post-procedure adverse event (post-endoscopic sphincterotomy bleeding). Within the median observation period of 312 days (range: 109-742), late adverse events, including cholangitis (n = 1) and incomplete stent migration (n = 1), were observed. However, none of the patients experienced cholecystitis relapse.
Conclusion: Permanent ETGBD with IYO-stent is an effective treatment for the patients with acute cholecystitis who are not indicated for surgery.
Keywords: acute cholecystitis; endoscopic transpapillary gallbladder drainage.
© 2021 The Authors. DEN Open published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japan Gastroenterological Endoscopy Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Clinical outcomes and predictors of technical failure of endoscopic transpapillary gallbladder drainage in acute cholecystitis.Scand J Gastroenterol. 2023 Mar;58(3):286-290. doi: 10.1080/00365521.2022.2118554. Epub 2022 Sep 7. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2023. PMID: 36069161
-
Endoscopic transpapillary gallbladder drainage for the management of acute calculus cholecystitis patients unfit for urgent cholecystectomy.PLoS One. 2020 Oct 9;15(10):e0240219. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0240219. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33035230 Free PMC article.
-
Endoscopic gallbladder drainage for acute cholecystitis with high-risk surgical patients between transduodenal and transpapillary stenting.Endosc Ultrasound. 2021 Nov-Dec;10(6):448-454. doi: 10.4103/EUS-D-20-00130. Endosc Ultrasound. 2021. PMID: 34782492 Free PMC article.
-
Endoscopic ultrasound-guided gallbladder drainage, transpapillary drainage, or percutaneous drainage in high risk acute cholecystitis patients: a systematic review and comparative meta-analysis.Endoscopy. 2020 Feb;52(2):96-106. doi: 10.1055/a-1020-3932. Epub 2019 Oct 23. Endoscopy. 2020. PMID: 31645067
-
Long-term outcomes of endoscopic transpapillary gallbladder drainage using a novel spiral plastic stent in acute calculus cholecystitis.BMC Gastroenterol. 2022 Dec 23;22(1):539. doi: 10.1186/s12876-022-02610-5. BMC Gastroenterol. 2022. PMID: 36564715 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Endoscopic transpapillary gallbladder drainage using a novel sphincterotome.Dig Endosc. 2025 Mar;37(3):297-299. doi: 10.1111/den.14943. Epub 2024 Oct 22. Dig Endosc. 2025. PMID: 39438418 Free PMC article.
-
Novel over-the-wire stent exchange technique with a loop cutter for endoscopic transpapillary gallbladder drainage in a complex anatomical case.Dig Endosc. 2025 Jun;37(6):714-716. doi: 10.1111/den.14996. Epub 2025 Jan 20. Dig Endosc. 2025. PMID: 39834003 Free PMC article.
-
Feasibility of a novel 5F plastic stent in endoscopic transpapillary gallbladder drainage for acute cholecystitis.Endosc Int Open. 2025 Jan 7;13:a24657130. doi: 10.1055/a-2465-7130. eCollection 2025. Endosc Int Open. 2025. PMID: 40012576 Free PMC article.
-
Endoscopic Gallbladder Drainage Conversion versus Conservative Treatment Following Percutaneous Gallbladder Drainage in High-Risk Surgical Patients.Gut Liver. 2024 Mar 15;18(2):348-357. doi: 10.5009/gnl230019. Epub 2023 Jul 17. Gut Liver. 2024. PMID: 37458066 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Okamoto K, Suzuki K, Takada T, et al. Tokyo Guidelines 2018: Flowchart for the management of acute cholecystitis. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 2018; 25: 55–72. - PubMed
-
- Wakabayashi G, Iwashita Y, Hibi T, et al. Tokyo Guidelines 2018: Surgical management of acute cholecystitis: Safe steps in laparoscopic cholecystectomy for acute cholecystitis (with videos). J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 2018; 25: 73–86. - PubMed
-
- Mori Y, Itoi T, Baron TH, et al. Tokyo Guidelines 2018: Management strategies for gallbladder drainage in patients with acute cholecystitis (with videos). J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 2018; 25: 87–95. - PubMed
-
- Itoi T, Itokawa F, Kurihara T. Endoscopic ultrasonography‐guided gallbladder drainage: Actual technical presentations and review of the literature (with videos). J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci 2011; 18: 282–6. - PubMed
-
- Inoue T, Okumura F, Kachi K, et al. Long‐term outcomes of endoscopic gallbladder stenting in high‐risk surgical patients with calculous cholecystitis (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc 2016; 83: 905–13. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
