Recent advances in facemask devices for in vivo sampling of human exhaled breath aerosols and inhalable environmental exposures
- PMID: 35310778
- PMCID: PMC8917876
- DOI: 10.1016/j.trac.2022.116600
Recent advances in facemask devices for in vivo sampling of human exhaled breath aerosols and inhalable environmental exposures
Abstract
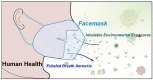
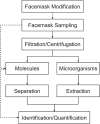
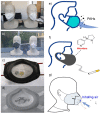
Since the COVID-19 pandemic, the unprecedented use of facemasks has been requiring for wearing in daily life. By wearing facemask, human exhaled breath aerosols and inhaled environmental exposures can be efficiently filtered and thus various filtration residues can be deposited in facemask. Therefore, facemask could be a simple, wearable, in vivo, onsite and noninvasive sampler for collecting exhaled and inhalable compositions, and gain new insights into human health and environmental exposure. In this review, the recent advances in developments and applications of in vivo facemask sampling of human exhaled bacteria, viruses, proteins, and metabolites, and inhalable facemask contaminants and air pollutants, are reviewed. New features of facemask sampling are highlighted. The perspectives and challenges on further development and potential applications of facemask devices are also discussed.
Keywords: Breath analysis; Breath sampling; COVID-19; Environmental exposures; Exhaled breath; Facemask; In vivo sampling; Inhalable exposures; Inhaled air; SARS-CoV-2.
© 2022 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The author declares that he has no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


References
-
- Papineni R.S., Rosenthal F.S. The size distribution of droplets in the exhaled breath of healthy human subjects. J. Aerosol Med. 1997;10:105–116. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
