60-Day PNS Treatment May Improve Identification of Delayed Responders and Delayed Non-Responders to Neurostimulation for Pain Relief
- PMID: 35310895
- PMCID: PMC8932923
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S349101
60-Day PNS Treatment May Improve Identification of Delayed Responders and Delayed Non-Responders to Neurostimulation for Pain Relief
Abstract
Objective: Conventional neurostimulation typically involves a brief (eg, ≤10-day) trial to assess presumed effectiveness prior to permanent implantation. Low trial conversion rates and high explant rates due to inadequate pain relief highlight the need for improved patient identification strategies. The development of a 60-day percutaneous peripheral nerve stimulation (PNS) system enables evaluation of outcomes following an extended temporary treatment period of up to 60 days, that may obviate or validate the need for permanent implant. The present study provides the first real-world evidence regarding patient response throughout a 60-day PNS treatment period.
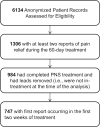
Methods: Anonymized data listings were compiled from patients who underwent implantation of temporary percutaneous leads and opted-in to provide real-world data to the device manufacturer during routine interactions with device representatives throughout the 60-day treatment.
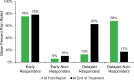
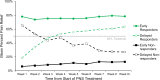
Results: Overall, 30% (222/747) of patients were early responders (≥50% pain relief throughout treatment). Another 31% (231/747) of patients initially presented as non-responders but surpassed 50% pain relief by the end of treatment. Conversely, 32% (239/747) of patients were non-responders throughout treatment. An additional 7% (55/747) of patients initially presented as responders but fell below 50% relief by the end of the treatment period.
Conclusion: An extended, 60-day PNS treatment may help identify delayed responders, providing the opportunity for sustained relief and improving access to effective PNS treatment. Compared to a conventionally short trial of ≤10 days, a longer 60-day PNS treatment may also help reduce explant rates by identifying delayed non-responders unlikely to benefit long-term. These scenarios support the importance of an extended 60-day temporary PNS stimulation period to help inform stepwise treatment strategies that may optimize outcomes and cost-effectiveness.
Keywords: 60-day PNS; chronic pain; neuromodulation; peripheral nerve stimulation; real-world evidence.
© 2022 Naidu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
R Naidu: research funding from Abbott, Boston Scientific, Nalu, Omnia Medical, and Vivex; consultant for Abbott, Avanos, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, CereVu, DoctorPlan, Exer AI, KarunaLabs, Medtronic, Nalu Medical, Omnia Medical, PainTEQ, SPR Therapeutics, and Vivex. S Li: research funding from Abbott, Avanos, Averitas Pharma, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, Nalu Medical, Nevro, PainTeq, Saluda Medical, SGX Medical, SPR Therapeutics; consultant for Avanos, Averitas Pharm, Biotronik, Boston Scientific, Nalu Medical, Nevro, PainTeq, Saluda Medical, Scilex Pharma, SPR Therapeutic, and Vertos; stock ownership/options in Nalu Medical, and National Spine and Pain Centers. MJ Desai: research funding from Abbott, Amgen, Bioness, Mainstay, Nalu, Nature Cell, Nevro, Seikagaku, SPR Therapeutics, and Vivex; consultant for Abbott, Avanos and Relievant; Stock ownership/options in SPR Therapeutics, SynerFuse, and Virdio. S Sheth: consultant for Nevro, Medtronic, Boston Scientific; speaker’s bureau for Medtronic; physician advisory board for Medtronic, Boston Scientific. ND Crosby: employee of SPR Therapeutics; stock ownership/options in SPR Therapeutics. JW Boggs: employee of SPR Therapeutics; stock ownership/options in SPR Therapeutics. He also has multiple patents owned by and issued to SPR Therapeutics. The authors report no other conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A review of prospective studies regarding percutaneous peripheral nerve stimulation treatment in the management of chronic pain.Pain Manag. 2024;14(4):209-222. doi: 10.1080/17581869.2024.2352398. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Pain Manag. 2024. PMID: 38939963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Retrospective Review of Real-world Outcomes Following 60-day Peripheral Nerve Stimulation for the Treatment of Chronic Pain.Pain Physician. 2023 May;26(3):273-281. Pain Physician. 2023. PMID: 37192232
-
Percutaneous Peripheral Nerve Stimulation for Chronic Low Back Pain: Prospective Case Series With 1 Year of Sustained Relief Following Short-Term Implant.Pain Pract. 2020 Mar;20(3):310-320. doi: 10.1111/papr.12856. Epub 2019 Dec 2. Pain Pract. 2020. PMID: 31693791 Free PMC article.
-
Is Response to a Pre-implant Diagnostic Peripheral Nerve Block Associated With Efficacy After Peripheral Nerve Stimulation Implantation? A Ten-Year Enterprise-Wide Analysis.Neuromodulation. 2024 Jul;27(5):873-880. doi: 10.1016/j.neurom.2023.10.003. Epub 2023 Nov 10. Neuromodulation. 2024. PMID: 37943242
-
Peripherally Induced Reconditioning of the Central Nervous System: A Proposed Mechanistic Theory for Sustained Relief of Chronic Pain with Percutaneous Peripheral Nerve Stimulation.J Pain Res. 2021 Mar 12;14:721-736. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S297091. eCollection 2021. J Pain Res. 2021. PMID: 33737830 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Beyond the Pain Management Clinic: The Role of AI-Integrated Remote Patient Monitoring in Chronic Disease Management - A Narrative Review.J Pain Res. 2024 Dec 11;17:4223-4237. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S494238. eCollection 2024. J Pain Res. 2024. PMID: 39679431 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A review of prospective studies regarding percutaneous peripheral nerve stimulation treatment in the management of chronic pain.Pain Manag. 2024;14(4):209-222. doi: 10.1080/17581869.2024.2352398. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Pain Manag. 2024. PMID: 38939963 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Peripheral Nerve Stimulation for Chronic Neuropathic Pain: A Health Technology Assessment.Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2024 Dec 3;24(10):1-131. eCollection 2024. Ont Health Technol Assess Ser. 2024. PMID: 39886278 Free PMC article.
-
Consensus Guidelines from the American Society of Pain and Neuroscience for the Use of 60-Day Peripheral Nerve Stimulation Therapy. A NEURON Living Guideline Project.J Pain Res. 2025 Jun 24;18:3117-3139. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S521788. eCollection 2025. J Pain Res. 2025. PMID: 40590046 Free PMC article.
-
Paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration combined with Lambert-Eaton myasthenia gravis syndrome in a patient positive for SOX1 antibody.Am J Transl Res. 2025 Apr 15;17(4):3001-3008. doi: 10.62347/NHTJ8584. eCollection 2025. Am J Transl Res. 2025. PMID: 40385046 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kuehn B. Chronic pain prevalence. JAMA. 2018;320(16):1632. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

