Long noncoding RNAs as promising biomarkers in cancer
- PMID: 35310927
- PMCID: PMC8891810
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ncrna.2022.02.004
Long noncoding RNAs as promising biomarkers in cancer
Abstract
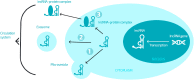
Despite many advances in diagnosis and therapy (surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy), cancer remains one of the most important public health problems worldwide. Every day, the role of exosomes in cancer development and metastasis is being better described. Liquid biopsy was developed for early detection of cancer through minimally invasive and serial examinations of body fluids, with the advantage of tracking tumor progression in real time. Exosomes are extracellular membrane vesicles with a diameter of 30-100 nm, which are secreted by various types of cells and are present in most biological fluids. For a long time, they were considered non-functional cellular components, and today it has already been proven that they are a means of intercellular information exchange. They can move bioactive molecules such as proteins, lipids, RNA and DNA. Several studies have shown that their contents, including proteins and noncoding nucleic acids, may be of particular interest as biomarkers of diseases. The vast majority of gene transcripts are actually characterized as noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) and are clusters of RNAs that do not encode functional proteins. They can be small, about 20 nucleotides in length, and are known as microRNAs (miRNAs), or transcripts over 200 nucleotides in length, defined as long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs). LncRNAs are a large group of ncRNAs over 200 nucleotides in length. LncRNAs, as regulatory factors, play an important role in complex cellular processes such as apoptosis, growth, differentiation, proliferation, etc. Recently, the results of many studies have also shown their essential role in carcinogenesis. Endogenous lncRNAs can be secreted by tumor cells into human biological fluids in the form of microvesicles, exosomes, or protein complexes, thereby forming circulating lncRNAs that are not degraded by RNA and are in a stable state. Aberrant expression of lncRNAs has been observed in cancer patients. In this context, endogenous lncRNAs can regulate the basic characteristics of cancer cells by controlling the expression of oncogenes associated with their suppressive and oncogenic functions. Therefore, circulating lncRNAs can be excellent biomarkers in cancer as well. This paper provides an overview of current research on the functional role of lncRNAs in cancer and their potential clinical applications as diagnostic biomarkers and therapeutic targets for cancer.
Keywords: Biomarker; Cancer; Exosomes; Pathogenesis; lncRNAs.
© 2022 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Siegel R.L., Miller K.D., Jemal A. Cancer statistics. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2016;66(1):10–29. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources