Pyroptosis-Related LncRNA Signature Predicts Prognosis and Is Associated With Immune Infiltration in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- PMID: 35311105
- PMCID: PMC8927701
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.794034
Pyroptosis-Related LncRNA Signature Predicts Prognosis and Is Associated With Immune Infiltration in Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Abstract
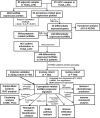
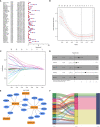
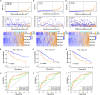
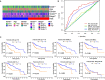
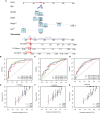
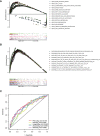
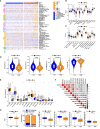
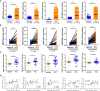
Pyroptosis is an inflammatory form of programmed cell death that is involved in various cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) were recently verified as crucial mediators in the regulation of pyroptosis. However, the role of pyroptosis-related lncRNAs in HCC and their associations with prognosis have not been reported. In this study, we constructed a prognostic signature based on pyroptosis-related differentially expressed lncRNAs in HCC. A co-expression network of pyroptosis-related mRNAs-lncRNAs was constructed based on HCC data from The Cancer Genome Atlas. Cox regression analyses were performed to construct a pyroptosis-related lncRNA signature (PRlncSig) in a training cohort, which was subsequently validated in a testing cohort and a combination of the two cohorts. Kaplan-Meier analyses revealed that patients in the high-risk group had poorer survival times. Receiver operating characteristic curve and principal component analyses further verified the accuracy of the PRlncSig model. Besides, the external cohort validation confirmed the robustness of PRlncSig. Furthermore, a nomogram based on the PRlncSig score and clinical characteristics was established and shown to have robust prediction ability. In addition, gene set enrichment analysis revealed that the RNA degradation, the cell cycle, the WNT signaling pathway, and numerous immune processes were significantly enriched in the high-risk group compared to the low-risk group. Moreover, the immune cell subpopulations, the expression of immune checkpoint genes, and response to chemotherapy and immunotherapy differed significantly between the high- and low-risk groups. Finally, the expression levels of the five lncRNAs in the signature were validated by quantitative real-time PCR. In summary, our PRlncSig model shows significant predictive value with respect to prognosis of HCC patients and could provide clinical guidance for individualized immunotherapy.
Keywords: hepatocellular carcinoma; immune infiltration; immunotherapy; long non-coding RNA; pyroptosis.
Copyright © 2022 Liu, Wu, Zhang, Kong, Shang, Lv, Li, Lu, Yong, Zhang, Zheng, Li, Chen, Bian and Wei.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Anoikis-related lncRNA signature predicts prognosis and is associated with immune infiltration in hepatocellular carcinoma.Anticancer Drugs. 2024 Jun 1;35(5):466-480. doi: 10.1097/CAD.0000000000001589. Epub 2024 Mar 11. Anticancer Drugs. 2024. PMID: 38507233
-
Identification and Validation of a Three Pyroptosis-Related lncRNA Signature for Prognosis Prediction in Lung Adenocarcinoma.Front Genet. 2022 Jul 19;13:838624. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.838624. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35928454 Free PMC article.
-
Screening prognostic markers for hepatocellular carcinoma based on pyroptosis-related lncRNA pairs.BMC Bioinformatics. 2023 Apr 29;24(1):176. doi: 10.1186/s12859-023-05299-9. BMC Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 37120506 Free PMC article.
-
A pyroptosis-related lncRNA signature predicts prognosis and immune microenvironment in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Dec;101(Pt B):108268. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2021.108268. Epub 2021 Oct 20. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34688154
-
NLRP6-Dependent Pyroptosis-Related lncRNAs Predict the Prognosis of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Med (Lausanne). 2022 Mar 2;9:760722. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2022.760722. eCollection 2022. Front Med (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35308537 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Role of Noncoding RNAs in the Tumor Immune Microenvironment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2023 Jun 28;11(3):682-694. doi: 10.14218/JCTH.2022.00412. Epub 2023 Jan 19. J Clin Transl Hepatol. 2023. PMID: 36969884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A pyroptosis-related lncRNA-based prognostic index for hepatocellular carcinoma by relative expression orderings.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Mar 31;13(3):1406-1424. doi: 10.21037/tcr-23-1804. Epub 2024 Mar 25. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 38617506 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Pyroptosis Is a Potential Therapeutic Strategy for Cancer.J Oncol. 2022 Nov 24;2022:2515525. doi: 10.1155/2022/2515525. eCollection 2022. J Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36467499 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noncoding RNA-mediated regulation of pyroptotic cell death in cancer.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 31;12:1015587. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.1015587. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36387211 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Construction of a Necroptosis-Associated Long Non-Coding RNA Signature to Predict Prognosis and Immune Response in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Front Mol Biosci. 2022 Jul 13;9:937979. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2022.937979. eCollection 2022. Front Mol Biosci. 2022. PMID: 35911976 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

