Lisinopril Mitigates Radiation-Induced Mitochondrial Defects in Rat Heart and Blood Cells
- PMID: 35311118
- PMCID: PMC8924663
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2022.828177
Lisinopril Mitigates Radiation-Induced Mitochondrial Defects in Rat Heart and Blood Cells
Abstract
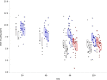
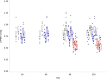
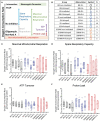
The genetic bases and disparate responses to radiotherapy are poorly understood, especially for cardiotoxicity resulting from treatment of thoracic tumors. Preclinical animal models such as the Dahl salt-sensitive (SS) rat can serve as a surrogate model for salt-sensitive low renin hypertension, common to African Americans, where aldosterone contributes to hypertension-related alterations of peripheral vascular and renal vascular function. Brown Norway (BN) rats, in comparison, are a normotensive control group, while consomic SSBN6 with substitution of rat chromosome 6 (homologous to human chromosome 14) on an SS background manifests cardioprotection and mitochondrial preservation to SS rats after injury. In this study, 2 groups from each of the 3 rat strains had their hearts irradiated (8 Gy X 5 fractions). One irradiated group was treated with the ACE-inhibitor lisinopril, and a separate group in each strain served as nonirradiated controls. Radiation reduced cardiac end diastolic volume by 9-11% and increased thickness of the interventricular septum (11-16%) and left ventricular posterior wall (14-15%) in all 3 strains (5-10 rats/group) after 120 days. Lisinopril mitigated the increase in posterior wall thickness. Mitochondrial function was measured by the Seahorse Cell Mitochondrial Stress test in peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) at 90 days. Radiation did not alter mitochondrial respiration in PBMC from BN or SSBN6. However, maximal mitochondrial respiration and spare capacity were reduced by radiation in PBMC from SS rats (p=0.016 and 0.002 respectively, 9-10 rats/group) and this effect was mitigated by lisinopril (p=0.04 and 0.023 respectively, 9-10 rats/group). Taken together, these results indicate injury to the heart by radiation in all 3 strains of rats, although the SS rats had greater susceptibility for mitochondrial dysfunction. Lisinopril mitigated injury independent of genetic background.
Keywords: cardiotoxicity; lisinopril; mitochondrial dysfunction; rat model; thoracic radiation.
Copyright © 2022 Ortiz de Choudens, Sparapani, Narayanan, Lohr, Gao, Fish, Zielonka, Gasperetti, Veley, Beyer, Olson, Jacobs and Medhora.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Mapping genetic modifiers of radiation-induced cardiotoxicity to rat chromosome 3.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019 Jun 1;316(6):H1267-H1280. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00482.2018. Epub 2019 Mar 8. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30848680 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in Expression of Mitochondrial Complexes Due to Genetic Variants May Alter Sensitivity to Radiation-Induced Cardiac Dysfunction.Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020 Mar 5;7:23. doi: 10.3389/fcvm.2020.00023. eCollection 2020. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2020. PMID: 32195269 Free PMC article.
-
Genetically determined mitochondrial preservation and cardioprotection against myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury in a consomic rat model.Physiol Genomics. 2014 Mar 1;46(5):169-76. doi: 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00118.2013. Epub 2013 Dec 31. Physiol Genomics. 2014. PMID: 24380873 Free PMC article.
-
Role of the CYP4A/20-HETE pathway in vascular dysfunction of the Dahl salt-sensitive rat.Clin Sci (Lond). 2013 Jun;124(12):695-700. doi: 10.1042/CS20120483. Clin Sci (Lond). 2013. PMID: 23438293 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lisinopril in the treatment of hypertension.J Hum Hypertens. 1989 Jun;3 Suppl 1:17-21. J Hum Hypertens. 1989. PMID: 2550640 Review.
Cited by
-
Preclinical models of radiation-induced cardiac toxicity: Potential mechanisms and biomarkers.Front Oncol. 2022 Oct 12;12:920867. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.920867. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 36313656 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Whole-Genome Sequence Analysis, Probiotic Potential, and Safety Assessment of the Marine Bacterium Paraliobacillus zengyii CGMCC1.16464.Mar Drugs. 2025 May 7;23(5):202. doi: 10.3390/md23050202. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40422792 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging mitochondrial signaling mechanisms in cardio-oncology: beyond oxidative stress.Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2022 Oct 1;323(4):H702-H720. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00231.2022. Epub 2022 Aug 5. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35930448 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Surveillance Epidemiology and End Results (SEER) Program . SEER Cancer Statistics Factsheets: Common Cancer Sites. National Cancer Institute Bethesda, MD. Available at: https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/common.html.
-
- Groarke JD, Nguyen PL, Nohria A, Ferrari R, Cheng S, Moslehi J. Cardiovascular Complications of Radiation Therapy for Thoracic Malignancies: The Role for Non-Invasive Imaging for Detection of Cardiovascular Disease. Eur Heart J (2014) 35(10):612–23. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/eht114 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

