Effects of polyphenol-rich traditional herbal teas on obesity and oxidative stress in rats fed a high-fat-sugar diet
- PMID: 35311163
- PMCID: PMC8907747
- DOI: 10.1002/fsn3.2695
Effects of polyphenol-rich traditional herbal teas on obesity and oxidative stress in rats fed a high-fat-sugar diet
Abstract
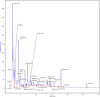
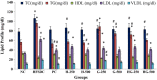
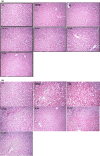
Hibiscus rosa-sinensis and Zingiber officinalis teas are traditionally used for the therapies of various diseases, including obesity. The present research work was planned to appraise the potential of polyphenol-rich extracts of selected herbal plants in obesity and related biochemical parameters of high-fat-sugar diet-induced obese rats. Three herbal teas were prepared from Hibiscus rosa-sinensis flowers and Zingiber officinalis rhizomes and their mixture (3:1, respectively). Total phenolic contents (TPC) of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis and Zingiber officinalis extracts were found to be 5.82 and 1.45 mg/g of dry plant material, measured as GAE, while total flavonoid contents (TFC) were 9.17 and 1.95 mg/g of dry plant material, measured as CE, respectively. Two doses (250 and 500 mg/kg BW) of each tea were administered and body weight, BMI, kidney, liver, and atherogenic indices, TC, TG, HDL, LDL, VLDL, BT, AST, ALT, AP, SC, MDA, SOD, GSH, and TAC of rats groups were measured. Data showed that higher doses of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis significantly reduced the rat's BMI (0.50 g/cm2) in comparison with the high-fat-sugar diet group (0.79 g/cm2). All treatment groups, especially H-500 group, showed a significant decrease in the elevated kidney and liver weights and atherogenic index in comparison with HFSDC groups. Higher doses of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis significantly decreased the levels of AST, ALT, AP, and SC in comparison with the HFSDC group. A significant decrease in the levels of serum TC, TG, LDL, and VLDL was observed in all the treatment groups in comparison with the HFSDC group. Furthermore, all the teas, especially higher doses of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis, prevented the alterations in MDA, SOD, and GSH levels of experimental groups, thus showing the potential against oxidative stress. It can be concluded from these results that Hibiscus rosa-sinensis teas exhibited strong protective effects against obesity and oxidative stress, especially at higher doses.
Keywords: BMI; GSH; LDL and HDL; MDA; SOD; high‐fat diet; kidney index; liver index; nutraceutical; phenolic acids and flavonoids.
© 2022 The Authors. Food Science & Nutrition published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they do not have any conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Bioprotective Effects of Marigold Tea Polyphenols on Obesity and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in High-Fat-Sugar Diet-Fed Rats.Cardiovasc Ther. 2024 Oct 4;2024:3833521. doi: 10.1155/2024/3833521. eCollection 2024. Cardiovasc Ther. 2024. PMID: 39742004 Free PMC article.
-
Antioxidant, Anti-Obesity, and Hypolipidemic Effects of Polyphenol Rich Star Anise (Illicium verum) Tea in High-Fat-Sugar Diet-Induced Obesity Rat Model.Antioxidants (Basel). 2022 Nov 14;11(11):2240. doi: 10.3390/antiox11112240. Antioxidants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36421427 Free PMC article.
-
Beneficial effects of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L. flower aqueous extract in pregnant rats with diabetes.PLoS One. 2017 Jun 23;12(6):e0179785. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179785. eCollection 2017. PLoS One. 2017. PMID: 28644857 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of Hibiscus rosa sinensis on reserpine-induced neurobehavioral and biochemical alterations in rats.Indian J Exp Biol. 2009 Jul;47(7):559-63. Indian J Exp Biol. 2009. PMID: 19761039
-
A Comprehensive Overview of Hibiscus rosa-sinensis L.: Its Ethnobotanical Uses, Phytochemistry, Therapeutic Uses, Pharmacological Activities, and Toxicology.Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2024;24(1):86-115. doi: 10.2174/1871530323666230522113405. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 37218183 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Goldenberry (Fruits with Husk) Extract in Ameliorating the Architecture and Osmotic Fragility of Red Blood Cells in Obese Rats.Biomed Res Int. 2023 Nov 27;2023:8794214. doi: 10.1155/2023/8794214. eCollection 2023. Biomed Res Int. 2023. PMID: 38054046 Free PMC article.
-
Phenolic Profile of Seedless Ziziphus mauritiana Fruits and Leaves Extracts with In Vivo Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities: Influence on Pro-Inflammatory Mediators.Chem Biodivers. 2025 Mar;22(3):e202401728. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.202401728. Epub 2024 Dec 12. Chem Biodivers. 2025. PMID: 39475065 Free PMC article.
-
The Bioprotective Effects of Marigold Tea Polyphenols on Obesity and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers in High-Fat-Sugar Diet-Fed Rats.Cardiovasc Ther. 2024 Oct 4;2024:3833521. doi: 10.1155/2024/3833521. eCollection 2024. Cardiovasc Ther. 2024. PMID: 39742004 Free PMC article.
-
Effectiveness of Aqueous Hibiscus Sabdariffa Extract on Reduction of Blood Pressure and Serum Lipids Among Prehypertensive Patients.J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2024 Jul;16(Suppl 3):S2886-S2888. doi: 10.4103/jpbs.jpbs_554_24. Epub 2024 Jul 18. J Pharm Bioallied Sci. 2024. PMID: 39346261 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactivity-Guided Isolation and Antihypertensive Activity of Citrullus colocynthis Polyphenols in Rats with Genetic Model of Hypertension.Medicina (Kaunas). 2023 Oct 23;59(10):1880. doi: 10.3390/medicina59101880. Medicina (Kaunas). 2023. PMID: 37893598 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Afify, A. E. M. R. , & Hassan, H. M. M. (2016). Free radical scavenging activity of three different flowers: Hibiscus rosa‐sinensis, Quisqualis indica and Senna surattensis . Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicines, 6, 771–777.
-
- ElRokh, E.‐S. , Yassin, N. A. Z. , El‐Shenawy, S. M. A. , & Ibrahim, B. M. M. (2010). Antihypercholesterolaemic effect of ginger rhizome (Zingiber officinale) in rats. Inflammopharmacology, 18, 309–315. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

