Long non-coding RNA NCK1-AS1 is overexpressed in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and predicts survival
- PMID: 35311444
- PMCID: PMC9162014
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2038449
Long non-coding RNA NCK1-AS1 is overexpressed in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma and predicts survival
Abstract
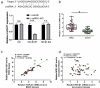
Long noncoding RNAs have shown pivotal regulatory roles in tumorigenesis and progression. NCK1-AS1 promotes cervical cancer, while its involvement in esophageal cancer is hardly known. This study enrolled 52 esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) patients (30 males and 22 females) at the average age of 56.4 ± 6.6 years in the range from 46 to 70 years, explored the involvement of NCK1-AS1 in ESCC, and analyzed the possible interaction between NCK1-AS1 and TGF-β signaling. Changes in gene expression were analyzed using RT-qPCR and Western blot. Interactions between gene expressions were analyzed using ESCC cells with transient transfections. Cell invasion and migration were analyzed using Transwell assays. Our data showed that plasma NCK1-AS1 was overexpressed in ESCC patients and positively correlated with NCK1-AS1 expression in tumor tissues but not in non-tumor tissues. Moreover, high plasma NCK1-AS1 levels were accompanied with poor survival. TGF-β1 expression level was also increased in tumor tissues compared to the adjacent normal tissues and positively correlated with NCK1-AS1 in tumor tissues. TGF-β1 overexpression in ESCC cells did not affect NCK1-AS1 expression, while NCK1-AS1 overexpression in ESCC cells upregulated TGF-β1. Moreover, TGF-β1 and NCK1-AS1 overexpression increased ESCC cell migration and invasion, while TGF-β inhibitor reduced the effects of NCK1-AS1 overexpression. Overall, NCK1-AS1 may promote ESCC by upregulating TGF-β1.
Keywords: Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma; TGF-β1; lncRNANCK1-AS1; regulation; survival.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures





References
-
- Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011. Mar-Apr;61(2):69–90. - PubMed
-
- Enzinger PC, Mayer RJ.. Esophageal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003. Dec 4;349(23):2241–2252. - PubMed
-
- Holmes RS, Vaughan TL. Epidemiology and pathogenesis of esophageal cancer. Semin Radiat Oncol. 2007. Jan;17(1):2–9. - PubMed
-
- Miyazaki T, Kato H, Fukuchi M, et al. EphA2 overexpression correlates with poor prognosis in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 2003. Feb 20;103(5):657–663. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
