Hsa_circ_0072008 regulates cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in cervical squamous cell carcinoma via miR-1305/helicase, lymphoid specific (HELLS) axis
- PMID: 35311456
- PMCID: PMC9161871
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2022.2048945
Hsa_circ_0072008 regulates cell proliferation, migration, and invasion in cervical squamous cell carcinoma via miR-1305/helicase, lymphoid specific (HELLS) axis
Abstract
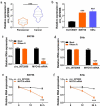
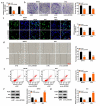
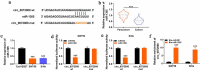
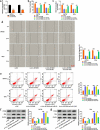
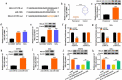
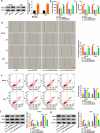
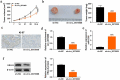
Cervical squamous cell carcinoma (CESC) is one of the most common cancers in women. Recent studies have proved that circular RNAs (circRNAs) could regulate the progress of CESC, but the mechanism is still indistinct. In this work, we explored the roles of circ_0072008 in CESC. The expression levels of circ_0072008, microRNA-1305 (miR-1305) and mRNA of HELLS (helicase, lymphoid specific) were detected by quantitative real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) in CESC tissues. Meanwhile, the level of HELLS was quantified by western blot analysis. Besides, the cell functions were examined by colony formation assay, 5-Ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine (EdU) assay, wound healing assay, flow cytometry assay and western blot. Furthermore, the interaction between miR-1305 and circ_0072008 or HELLS was detected by dual-luciferase reporter assay. The function of circ_0072008 in CESC has also been further verified in vivo by xenograft model experiments. The levels of circ_0072008 and HELLS were upregulated, and the miR-1305 level was decreased in CESC tissues in contrast to that in normal tissues. For functional analysis, silencing circ_0072008 inhibited cell proliferation and cell migration, whereas enhanced cell apoptosis in CESC cells. In mechanism, circ_0072008 acted as a miR-1305 sponge to regulate the level of HELLS. Moreover, miR-1305 was confirmed to repress the progression of CESC cells by suppressing HELLS. Meanwhile, knockdown of circ_0072008 inhibited CESC cells growth in vivo. In conclusion, circ_0072008 facilitated CESC cell proliferation, migration, and invasion through increasing HELLS expression by regulating miR-1305, which also offered an underlying targeted therapy for CESC treatment.
Keywords: Cervical squamous cell carcinoma; HELLS; circ_0072008; miR-1305.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hsa_circ_0016788 regulates hepatocellular carcinoma progression via miR-506-3p/poly-adenosine diphosphate-ribose polymerase.J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021 Dec;36(12):3457-3468. doi: 10.1111/jgh.15635. Epub 2021 Aug 23. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021. PMID: 34340259
-
Hsa_circ_0001495 contributes to cervical cancer progression by targeting miR-526b-3p/TMBIM6/mTOR axis.Reprod Biol. 2022 Jun;22(2):100648. doi: 10.1016/j.repbio.2022.100648. Epub 2022 May 6. Reprod Biol. 2022. PMID: 35533615
-
Knockdown of circ_0011946 targets miR-216a-5p/BCL2L2 axis to regulate proliferation, migration, invasion and apoptosis of oral squamous cell carcinoma cells.BMC Cancer. 2021 Oct 7;21(1):1085. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08779-4. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34620126 Free PMC article.
-
Circ_0025908 regulates cell vitality and proliferation via miR-137/HIPK2 axis of rheumatic arthritis.J Orthop Surg Res. 2021 Jul 30;16(1):472. doi: 10.1186/s13018-021-02615-y. J Orthop Surg Res. 2021. PMID: 34330307 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of hsa_circ_0009035 Suppresses Cervical Cancer Progression and Enhances Radiosensitivity through MicroRNA 889-3p-Dependent Regulation of HOXB7.Mol Cell Biol. 2021 May 21;41(6):e0063120. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00631-20. Epub 2021 May 21. Mol Cell Biol. 2021. PMID: 33782039 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Lymphoid-specific helicase inhibits cervical cancer cells ferroptosis by promoting Nrf2 expression.PeerJ. 2023 Nov 28;11:e16451. doi: 10.7717/peerj.16451. eCollection 2023. PeerJ. 2023. PMID: 38047020 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cohen PA, Jhingran A, Oaknin A, et al. Cervical cancer. Lancet. 2019;393:169–182. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. - PubMed
-
- Liu X, Min S, Wu N, et al. miR-193a-3p inhibition of the Slug activator PAK4 suppresses non-small cell lung cancer aggressiveness via the p53/Slug/L1CAM pathway. Cancer Lett. 2019;447:56–65. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
