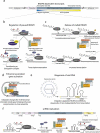
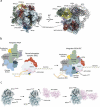
Emerging insights into the function and structure of the Integrator complex
- PMID: 35311473
- PMCID: PMC9006982
- DOI: 10.1080/21541264.2022.2047583
Emerging insights into the function and structure of the Integrator complex
Abstract
The Integrator was originally discovered as a specialized 3'-end processing endonuclease complex required for maturation of RNA polymerase II (RNAPII)-dependent small nuclear RNAs (snRNAs). Since its discovery, Integrator's spectrum of substrates was significantly expanded to include non-polyadenylated long noncoding RNAs (lncRNA), enhancer RNAs (eRNAs), telomerase RNA (tertRNA), several Herpesvirus transcripts, and messenger RNAs (mRNAs). Recently emerging transcriptome-wide studies reveled an important role of the Integrator in protein-coding genes, where it contributes to gene expression regulation through promoter-proximal transcription attenuation. These new functional data are complemented by several structures of Integrator modules and higher-order complexes, providing mechanistic insights into Integrator-mediated processing events. In this work, we summarize recent progress in our understanding of the structure and function of the Integrator complex.
Keywords: 3’-end processing; Integrator; RNAPII; cryo-EM; endonuclease; snRNA; transcription attenuation.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures
Similar articles
-
Integrator mediates the biogenesis of enhancer RNAs.Nature. 2015 Sep 17;525(7569):399-403. doi: 10.1038/nature14906. Epub 2015 Aug 26. Nature. 2015. PMID: 26308897 Free PMC article.
-
Integrator, a multiprotein mediator of small nuclear RNA processing, associates with the C-terminal repeat of RNA polymerase II.Cell. 2005 Oct 21;123(2):265-76. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.08.019. Cell. 2005. PMID: 16239144
-
Genomic regulation of transcription and RNA processing by the multitasking Integrator complex.Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023 Mar;24(3):204-220. doi: 10.1038/s41580-022-00534-2. Epub 2022 Sep 30. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023. PMID: 36180603 Free PMC article. Review.
-
IntS6 and the Integrator phosphatase module tune the efficiency of select premature transcription termination events.Mol Cell. 2023 Dec 21;83(24):4445-4460.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2023.10.035. Epub 2023 Nov 22. Mol Cell. 2023. PMID: 37995689 Free PMC article.
-
The Integrator complex: an emerging complex structure involved in the regulation of gene expression by targeting RNA polymerase II.Funct Integr Genomics. 2024 Oct 19;24(6):192. doi: 10.1007/s10142-024-01479-9. Funct Integr Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39424688 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome Assembly of a Relict Arabian Species of Daphnia O. F. Müller (Crustacea: Cladocera) Adapted to the Desert Life.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 3;24(1):889. doi: 10.3390/ijms24010889. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36614331 Free PMC article.
-
A combinatorial approach to uncover an additional Integrator subunit.Cell Rep. 2023 Mar 28;42(3):112244. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2023.112244. Epub 2023 Mar 14. Cell Rep. 2023. PMID: 36920904 Free PMC article.
-
Structural basis of Integrator-dependent RNA polymerase II termination.Nature. 2024 May;629(8010):219-227. doi: 10.1038/s41586-024-07269-4. Epub 2024 Apr 3. Nature. 2024. PMID: 38570683 Free PMC article.
-
Automated profiling of gene function during embryonic development.Cell. 2024 Jun 6;187(12):3141-3160.e23. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.04.012. Epub 2024 May 16. Cell. 2024. PMID: 38759650 Free PMC article.
-
Flipons and small RNAs accentuate the asymmetries of pervasive transcription by the reset and sequence-specific microcoding of promoter conformation.J Biol Chem. 2023 Sep;299(9):105140. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105140. Epub 2023 Aug 5. J Biol Chem. 2023. PMID: 37544644 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Baillat D, Hakimi M-A, Näär AM, et al. Integrator, a Multiprotein Mediator of Small Nuclear RNA Processing, Associates with the C-Terminal Repeat of RNA Polymerase II. Cell. 2005;123(2):265–276. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources